Search Results
Results for: 'polar bond'
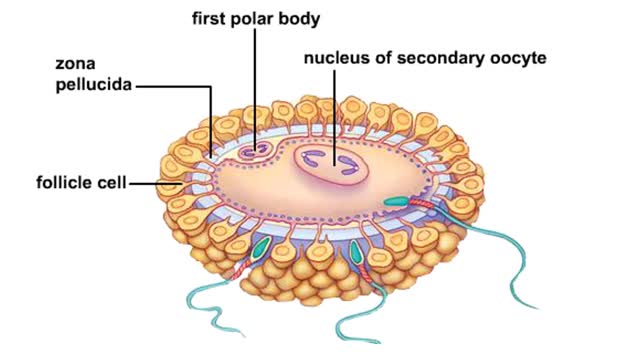
Rh blood type and complications during pregnancy & Fertilization
By: HWC, Views: 8530
Complications can arise if an Rh- woman is impregnated by an Rh+ man. The fetus maybe Rh+. During childbirth, some of the fetal Rh+ cells may leak into the maternal bloodstream. The woman's immune system views the Rh+ as foreign and makes antibodies against it. If the woman becomes pr...
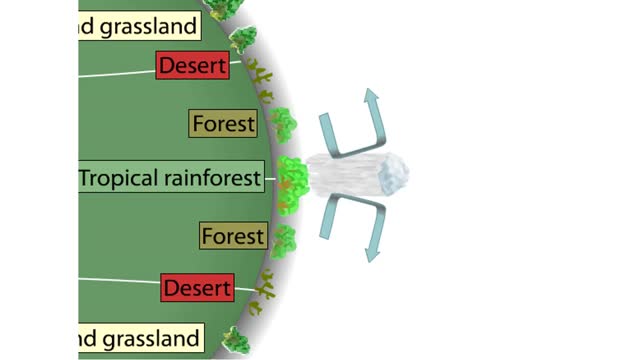
Four Giant Convection Cells oF Earth
By: HWC, Views: 10275
Earth Has Four Giant Convection Cells Earth's climates range from dry and cold at the poles to wet and warm at the equator. These climates are dictated largely by the amount of solar radiation that a region receives. Solar radiation warms the Earth and the surrounding air, setting up convection c...
By: HWC, Views: 10798
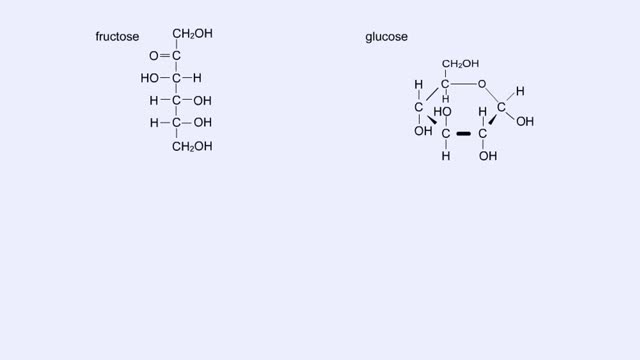
Here are the molecular structures of three simple sugars: glucose, ribose, and fructose. Look at these simple sugars and identify what characteristics they all share. As you can see, all of the carbohydrates have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 and there is always a double bo...
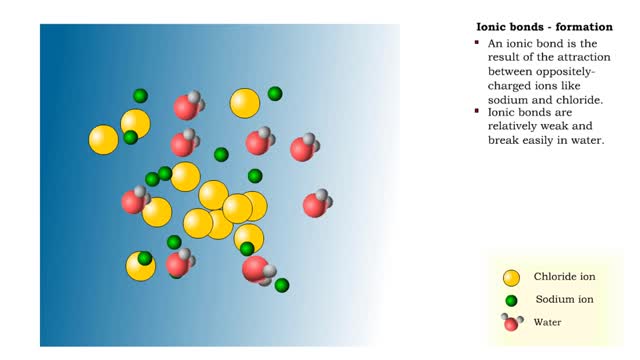
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11293
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
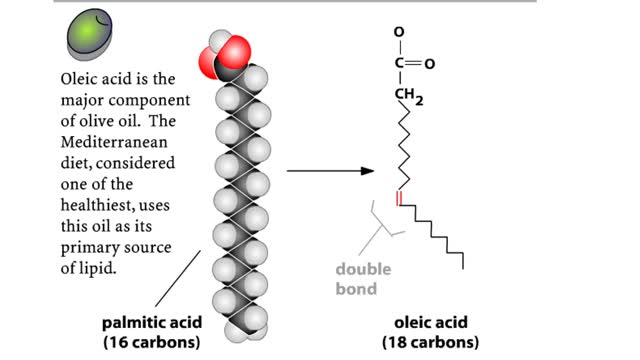
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Lipids
By: HWC, Views: 10417
A triglyceride (also called triacylglycerol) is composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. The fatty acids attach to the glycerol molecule by a covalent ester bond. The long hydrocarbon chain of each fatty acid makes the triglyceride molecule nonpolar and hydrophobic. Pa...
By: HWC, Views: 10840
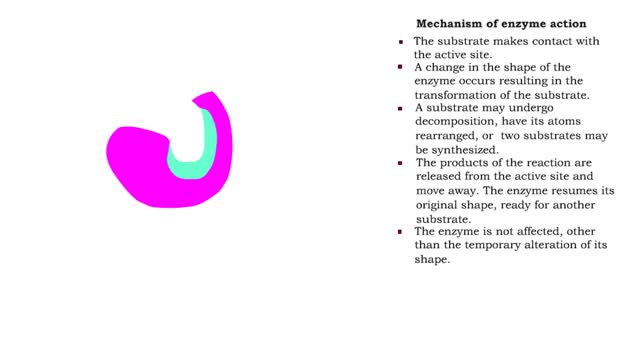
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
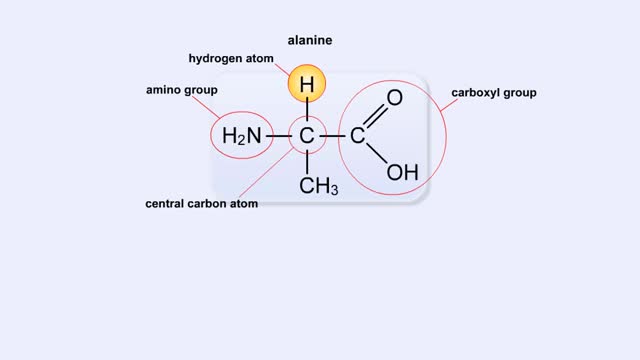
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 10633
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
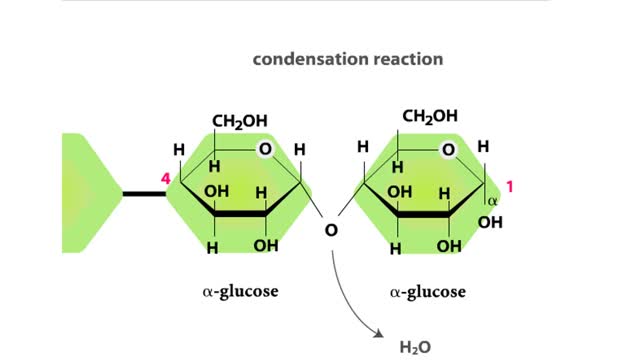
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC, Views: 10611
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be ...
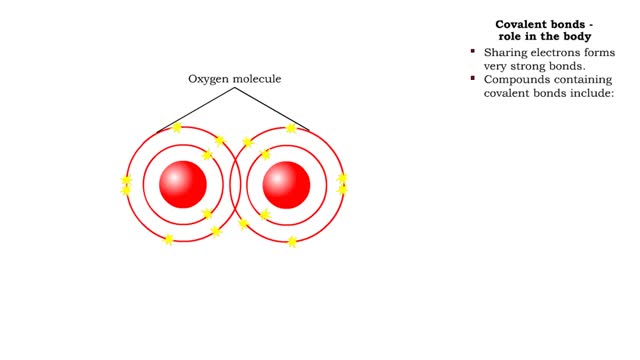
Covalent bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 10999
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This is opposed to an ionic bond, where electrons are actually transferred from one atom to another. Formation • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by sharing electrons. • Two oxygen atoms sharing electrons form on...
Advertisement