Search Results
Results for: 'systemic vascular resistance'
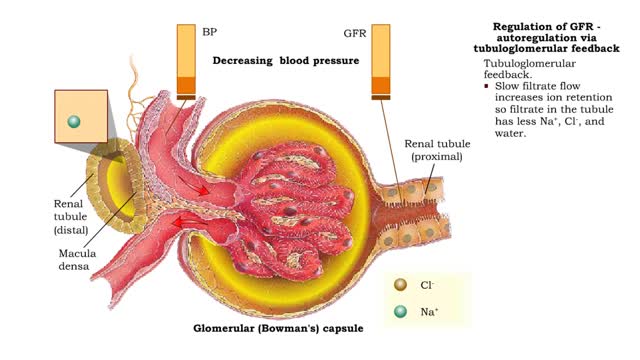
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12591
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
Introduction to Erectile Dysfunction
By: Administrator, Views: 370
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence, is a type of sexual dysfunction characterized by the inability to develop or maintain an erection of the penis during sexual activity. Erectile dysfunction can have psychological consequences as it can be tied to relationship difficulties and se...
By: Administrator, Views: 14265
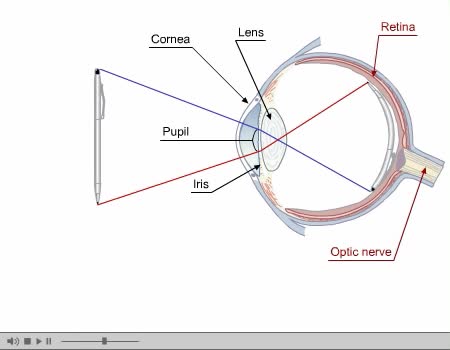
Eye Composed of special anatomical structures that work together to facilitate sight: Cornea Pupil Lens Vitreous body Light stimulates sensory receptors (rods and cones) in the retina or innermost layer of the eye. Vision is made possible through the coordinated actions of nerves that co...
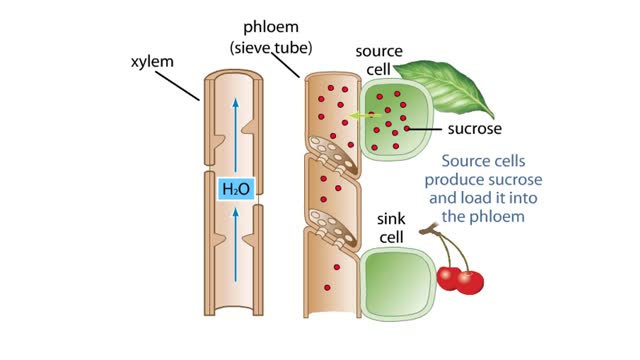
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10414
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
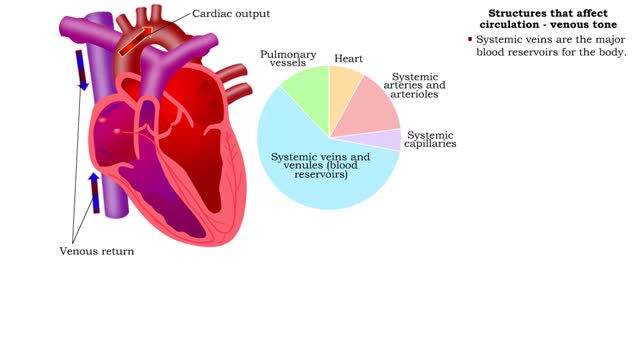
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys, blood volume and venous tone
By: HWC, Views: 11064
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
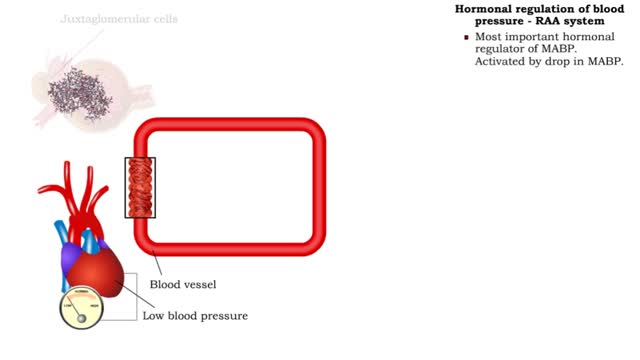
Hormonal regulation of blood pressure - RAA system
By: HWC, Views: 11543
■ Long-term regulation of MABP is under hormonal control. • Hormones that affect blood pressure and volume: the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system, antidiuretic hormone (ADM), and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). ■ Most important hormonal regulator of MABP. Activated by drop in...
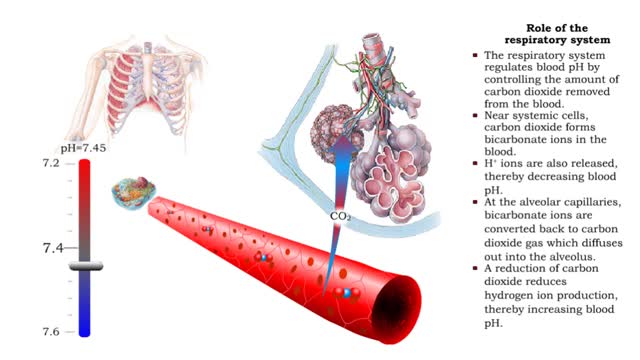
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 11627
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate io...
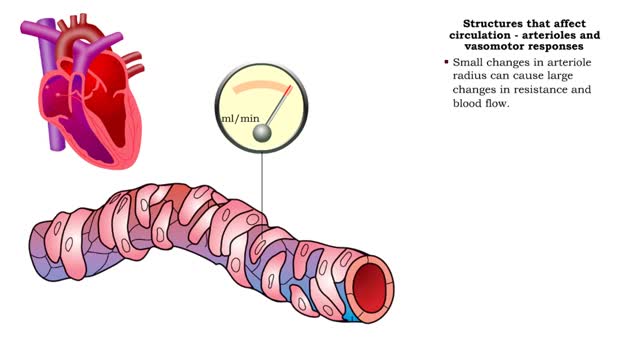
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses
By: HWC, Views: 10670
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. ■ Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. ■ Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
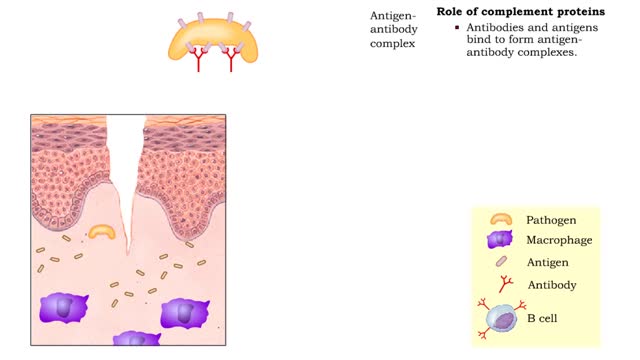
By: HWC, Views: 10811
• Non-specific and specific defense mechanisms work through the functions of complement proteins. • As soon as pathogens penetrate the physical barrier of the skin, other resistance mechanisms begin. • Cells, such as macrophages, phagocytize pathogens. • These cells increase exposu...
Advertisement