Search Results
Results for: 'contraction'
By: Administrator, Views: 14200
Status epilepticus (SE) is a single epileptic seizure lasting more than five minutes or two or more seizures within a five-minute period without the person returning to normal between them. Previous definitions used a 30-minute time limit. The seizures can be of the tonic–clonic type, with a re...
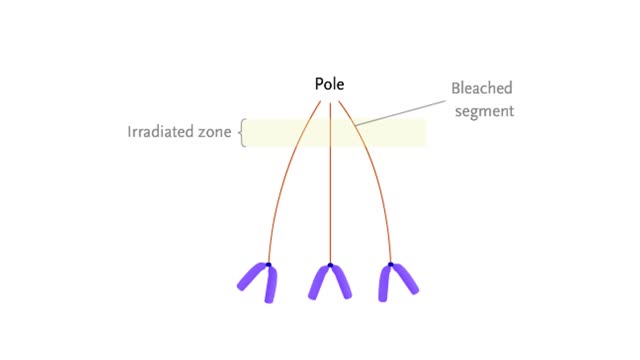
Mechanisms for chromosome movement Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8253
At mitotic metaphase, the fully-formed spindle is composed of many microtubules that extend from the poles. Some of these, the kinetochore microtubules, are attached to the kinetochores of each chromosome. Kinetochores are located at the centromeres. At anaphase, sister chromatids separate and...
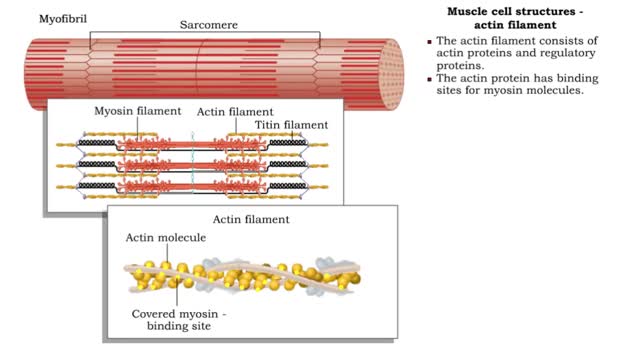
Muscle cell structures - actin, myosin and titin filaments
By: HWC, Views: 11380
Once the muscle cell has been excited it will contract. • A muscle action potential will trigger the release Of Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm. • The Ca2+ ions bind to the regulatory proteins and trigger contraction. • Within skeletal muscle cells are structures that provide the ability...
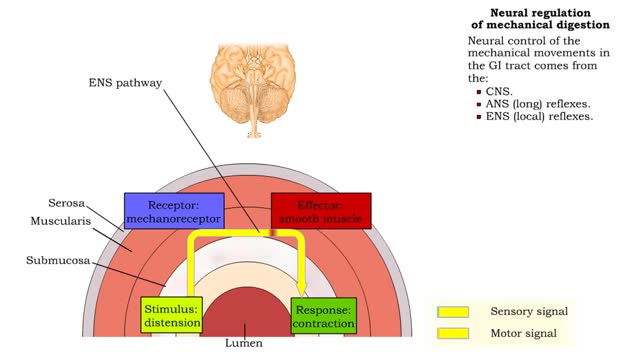
Neural regulation of mechanical digestion- CNS voluntary, ANS & ENS controlled involuntary movements
By: HWC, Views: 11065
• The gastrointestinal [GI] tract is basically a muscular tube that contains and processes food as it moves from the mouth to the anus. • Mechanical digestive functions consist of both voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions and relaxation including: • Chewing and swallowing food....
By: HWC, Views: 11331
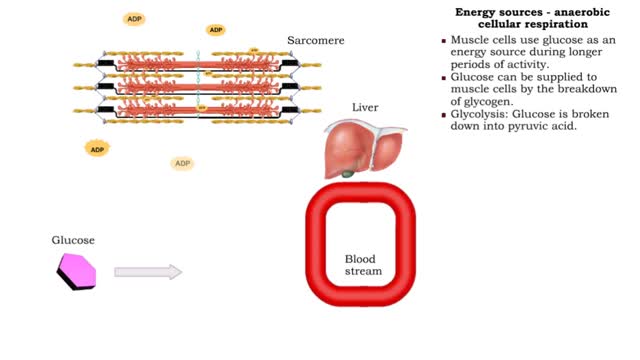
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen syste...
By: HWC, Views: 10730
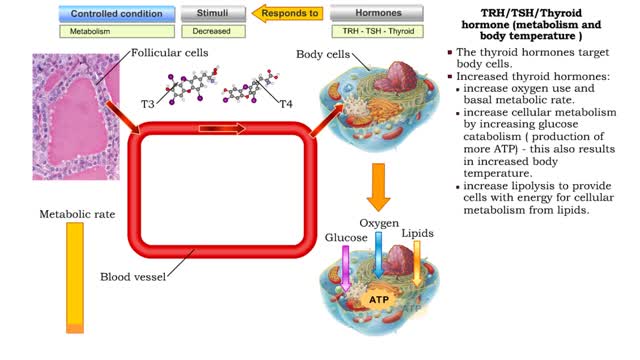
Thyroid hormone production • A decline in metabolic rate caused by increased metabolic need or physical exertion stimulates the production of thyrotropin hormone releasing (TRH) hormone from the cells of the hypothalamus. • Thyrotropin hormone releasing hormone targets the thyrotrophic ce...
Chromosome structural organization/ Mechanisms for chromosome movement Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7376
How the chromosome is organized. At metaphase, the chromosomes are duplicated and are at their most condensed. In each chromosome, two identical sister chromatids are held together at a constricted region called the centromere. When a chromosome is condensed, interactions among chromosomal ...
How proteins function? How do proteins work?
By: HWC, Views: 10792
How proteins function is really about how proteins "do work" in cells. How do proteins work? Let's start thinking about protein function by looking at something important to you: your hair. Keratin is a structural protein that is composed of 2 intertwined or helical strands. Keratin is also f...
Advertisement