Search Results
Results for: 'calcium ions'
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 9900
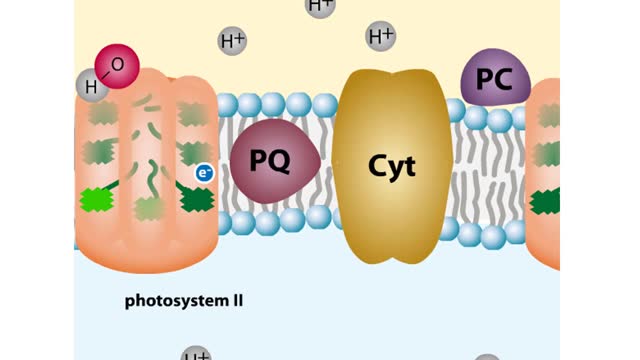
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10539
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
Stroke volume - contractility definition
By: HWC, Views: 10552
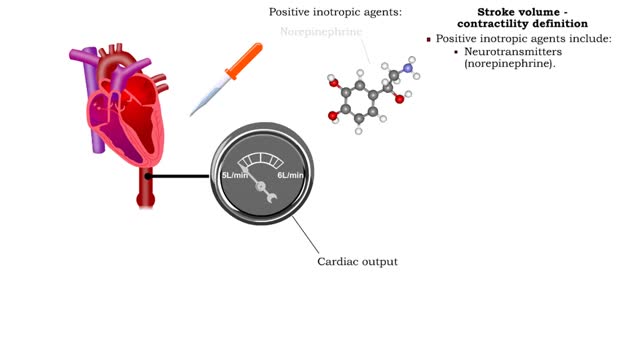
Contractility is the forcefulness of contraction of cardiac muscle. • Inotropic agents are substances that increase or decrease contractility (and stroke volume). • Positive inotropic agents increase contractility and will increase stroke volume and cardiac output. • Negative inotropi...
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 8216
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
Oxygen transport: association and dissociation & Factors that affect hemoglobin's saturation with O2
By: HWC, Views: 10801
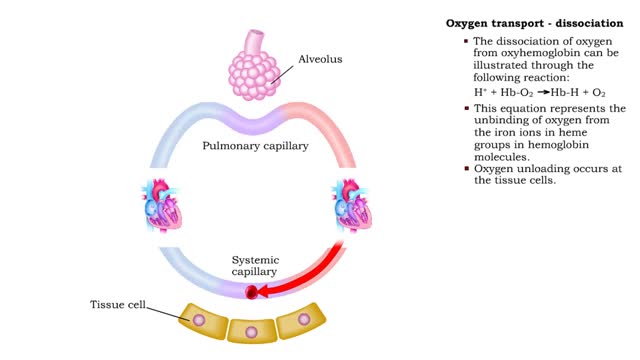
• The production of oxyhemoglobin can be illustrated through the following reaction: 02 + Hb-H --) Hb-02 + H+ • This equation represents the binding of oxygen to the iron ions in heme groups in hemoglobin molecules. • Oxygen binding or loading occurs at the lungs • The dissociatio...
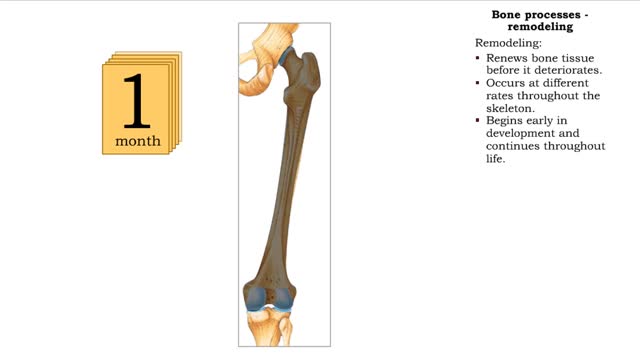
Bone processes - resorption and deposition, remodeling and response to stress in adult bones
By: HWC, Views: 11111
• The process of remodeling bone tissues involves bone cells resorbing or depositing minerals into bone tissue. • During resorption, bone cells break down bone tissue and release calcium and other minerals for use by other cells in the body. • Bone cells also rebuild bone tissue by depo...
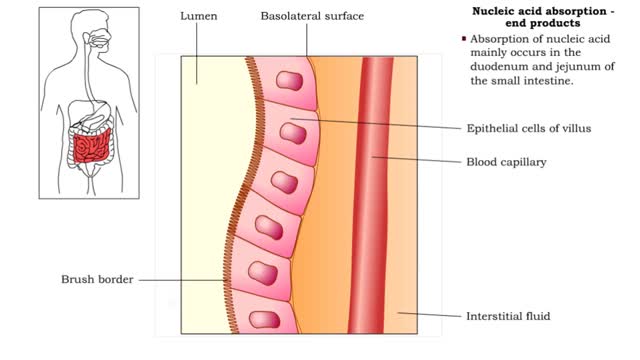
Nucleic acid digestion - brush border enzymes, end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 10691
• Further digestion occurs at the microvilli (brush border) of the epithelial cells of the villi in the small intestine. • Two brush border enzymes complete nucleic acid digestion: • Phosphatases, which catalyze the cleavage of a phosphate to form a nucleoside (nitrogenous base and pent...
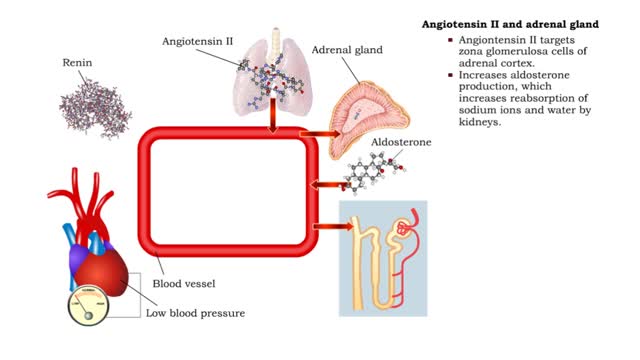
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 10963
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
By: HWC, Views: 11669
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Advertisement