Search Results
Results for: 'chloride ions'
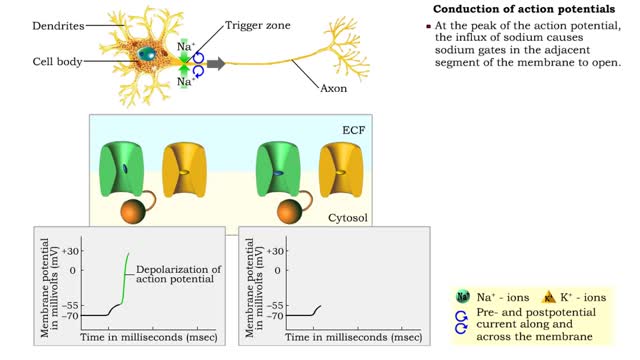
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11052
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
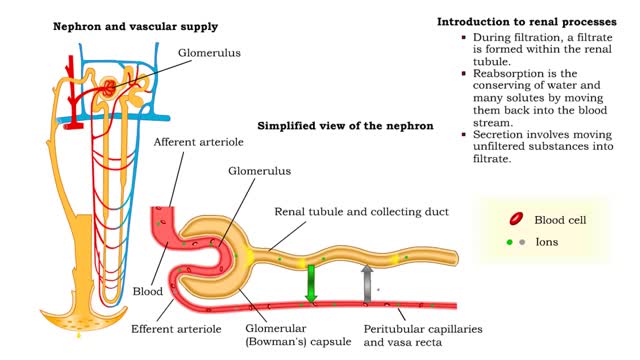
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Introduction to renal processes and filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 11048
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
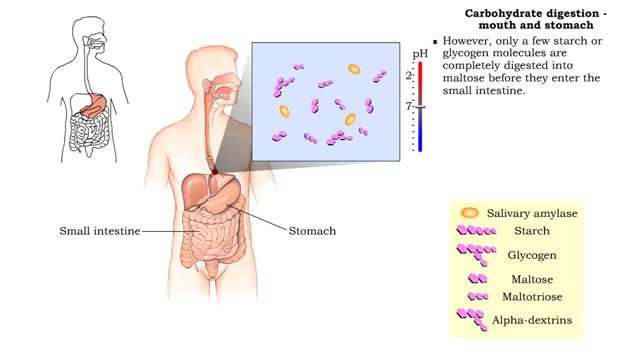
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 10734
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. �...
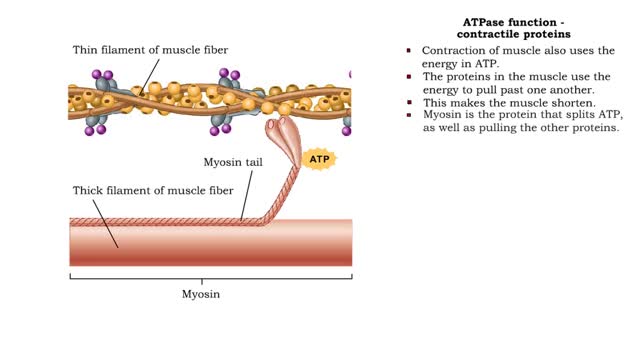
ATPase function - membrane transport, contractile proteins and synthesis
By: HWC, Views: 11308
• Energy from ATP is used to move ions across the cell membrane during active transport. • This membrane protein transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. As such, it is called a sodium-potassium pump. • Because this pump also acts as an enzyme to hydrolyze ATP it i...
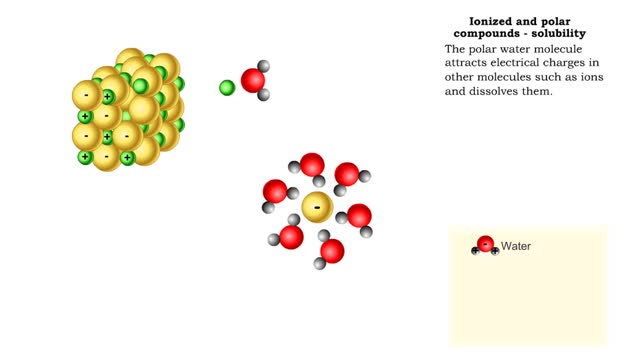
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 11032
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
Second Messengers in the Inositol-lipid Signaling Pathway
By: HWC, Views: 10052
Extracellular signals produce specific responses in target cells through the action of intracellular second messengers. Here, we focus on three second messengers, IP3, DAG, and Ca2+, all involved in the inositol-lipid signaling pathway. A hormone-receptor signal on the cell surface leads to the a...
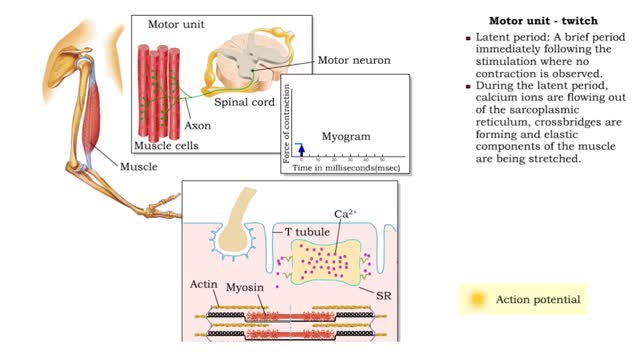
Muscle Twitch and Muscle Tension - Motor unit size and force
By: HWC, Views: 11105
• A motor unit is a group of muscle cells controlled by a single neuron. • A stimulus of sufficient intensity will cause all the cells in the motor unit to contract. • A single contraction, caused by a single action potential, is called a muscle twitch. • Latent period: A brief per...
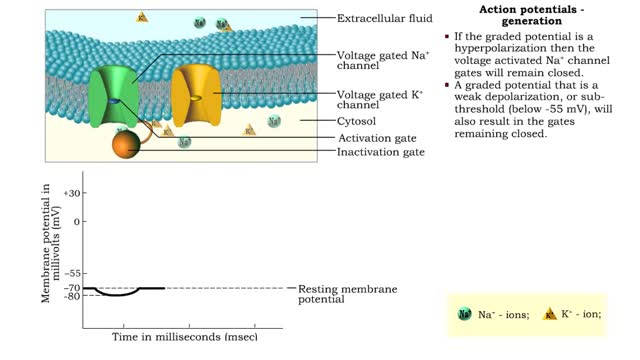
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 10724
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
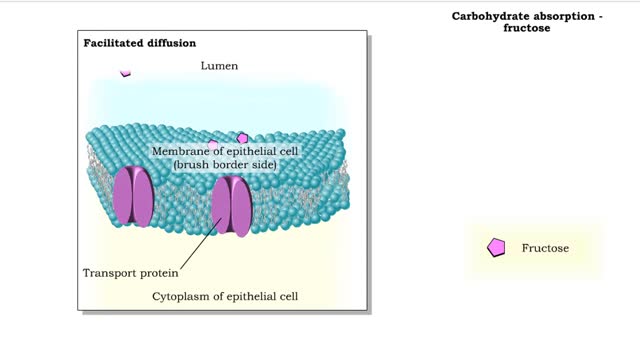
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 10794
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
Advertisement