Search Results
Results for: 'chloride ions'
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 8449
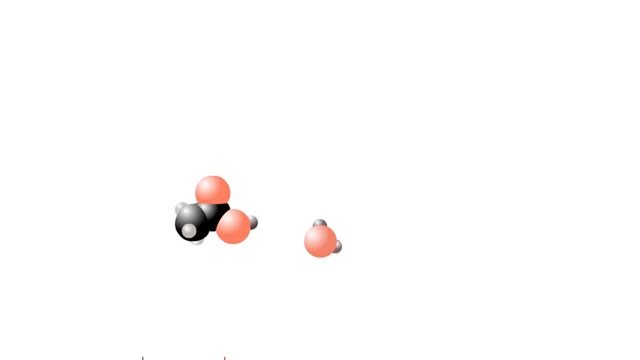
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
By: HWC, Views: 8432
The slight positive charge of a hydrogen atom in a water molecule can attract an atom with a slight negative charge, such as the nitrogen in a molecule of ammonia. This forms a hydrogen bond between the two atoms. Hydrogen bonds join the two strands of a DNA molecule. Although hydrogen bo...
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 9696
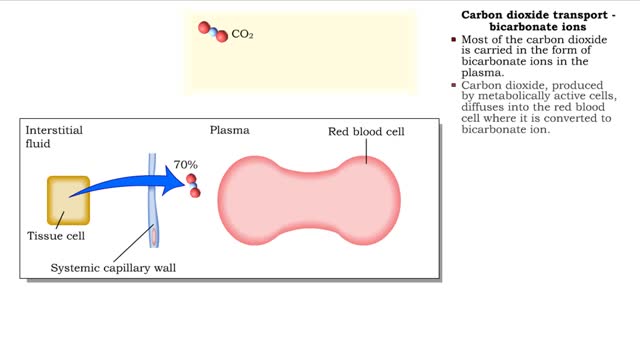
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 6985
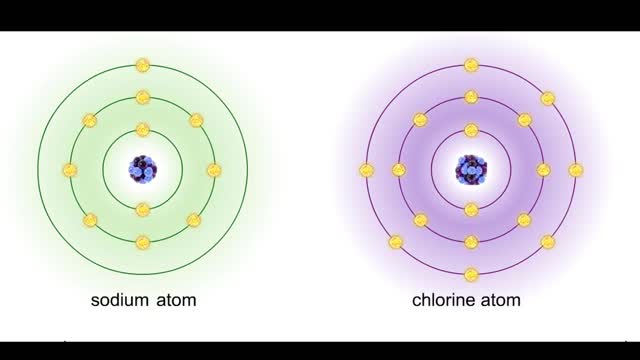
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
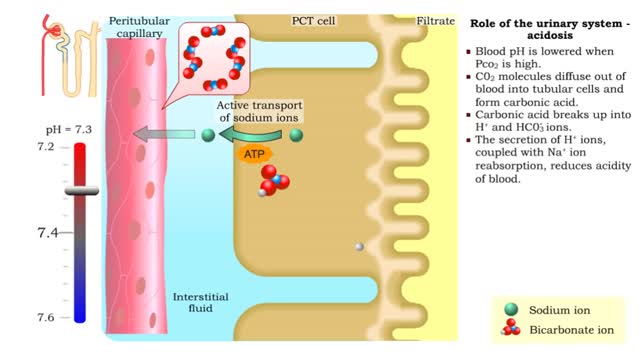
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 9873
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
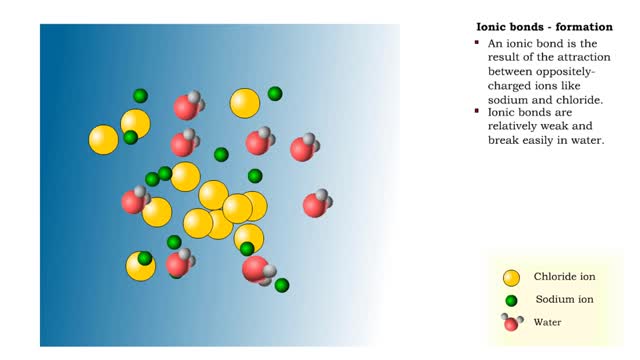
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 9938
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
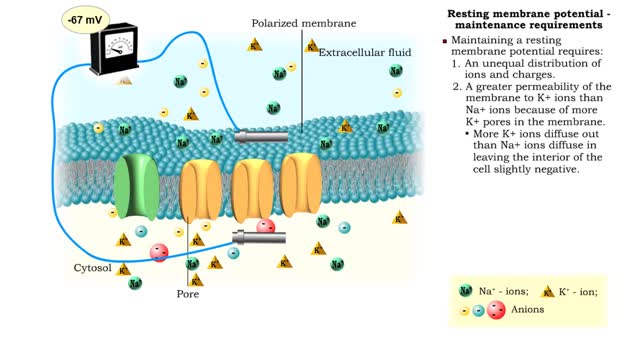
Resting membrane potential - electrical polarity and maintenance requirements
By: HWC, Views: 9378
• A resting membrane potential exists when there is a buildup of: 1. positive ions outside the membrane. 2. negative ions inside the membrane. • Membranes with opposing charges are said to be polarized. • The difference in charge applies only to the small distance across the membran...
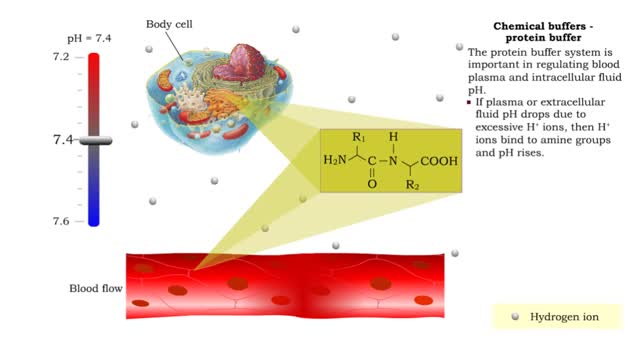
Chemical Buffers - protein buffer, phosphate buffer system and bicarbonate buffer system
By: HWC, Views: 9907
• There are a variety of chemicals in body fluids that prevent the fluids from undergoing large changes in. • These chemicals buffer or regulate fluctuations in H+ concentration. • Chemical buffers: • Bind to H+ ions when there are too many in a solution so pH remains normal. •...
By: HWC, Views: 10446
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Advertisement