Search Results
Results for: 'tubulin protein subunits'
By: HWC, Views: 10080
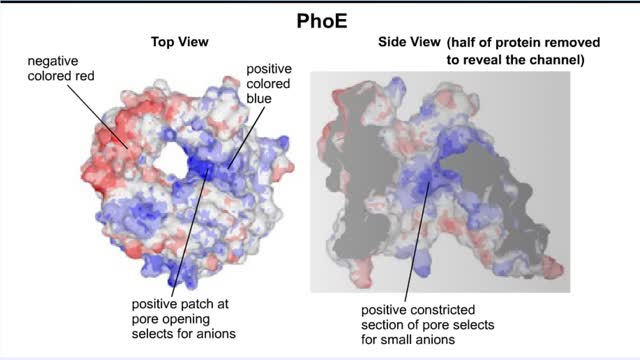
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 10696
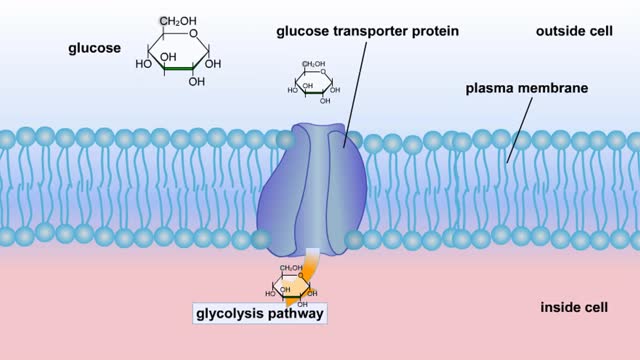
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 10815
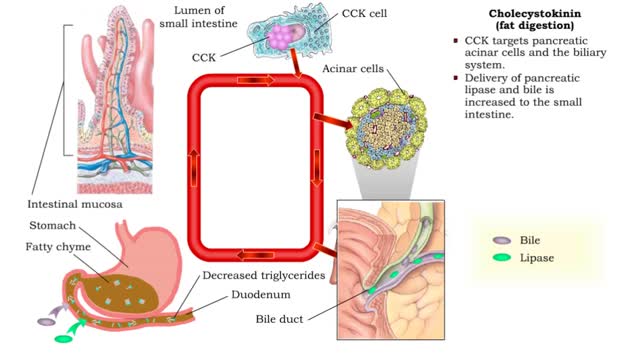
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
Chronology of leptin research (A history of leptin research)
By: HWC, Views: 8002
In 1950. researchers at Jackson Laboratories noticed that one of their mice had become extremely obese—it had an insatiable appetite. Intrigued, they bred a strain of mice showing this characteristic. In the late 1960s, researchers surgically connected the bloodstreams of a normal mouse and a...
Hormonal regulation of pregnancy - weeks 17 through 38
By: HWC, Views: 11193
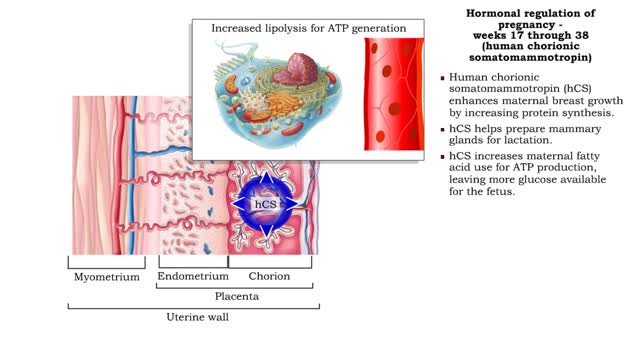
• Estrogens increase uterine blood flow, maintaining the endometrium during pregnancy. • High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit the synthesis of milk. Progesterone inhibits myometrial contractions of the uterus to prevent premature birth. • Relaxin inhibits myometrial contract...
Membrane Protein and Facilitated Transport (Passive Vs Active)
By: HWC, Views: 10544
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins span the membrane, with hydrophobic amino acids interacting with the lipid bilayer and hy...
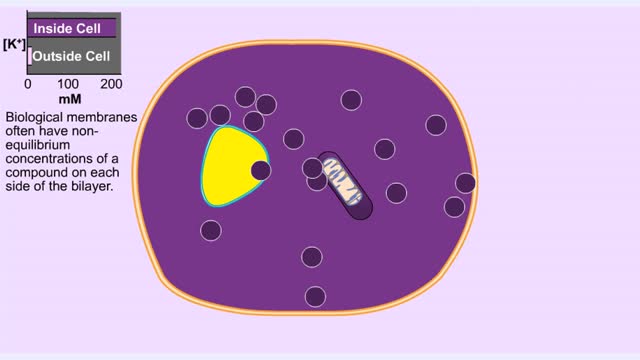
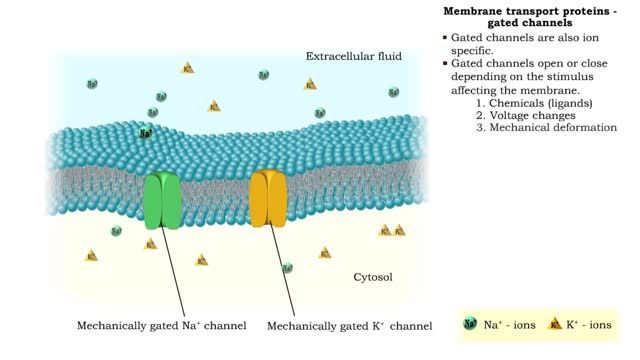
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11090
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
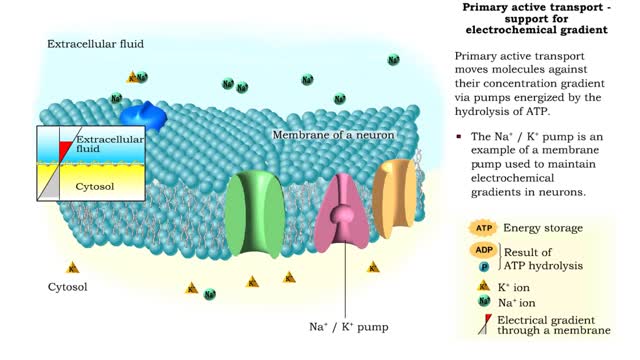
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 11114
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
By: HWC, Views: 9730
The slight positive charge of a hydrogen atom in a water molecule can attract an atom with a slight negative charge, such as the nitrogen in a molecule of ammonia. This forms a hydrogen bond between the two atoms. Hydrogen bonds join the two strands of a DNA molecule. Although hydrogen bo...
Advertisement