Search Results
Results for: 'Oxygen transport'
By: Administrator, Views: 14366
A heart attack occurs when an artery supplying your heart with blood and oxygen becomes blocked. Fatty deposits build up over time, forming plaques in your heart's arteries. If a plaque ruptures, a blood clot can form and block your arteries, causing a heart attack.
Bone processes - resorption and deposition, remodeling and response to stress in adult bones
By: HWC, Views: 11294
• The process of remodeling bone tissues involves bone cells resorbing or depositing minerals into bone tissue. • During resorption, bone cells break down bone tissue and release calcium and other minerals for use by other cells in the body. • Bone cells also rebuild bone tissue by depo...
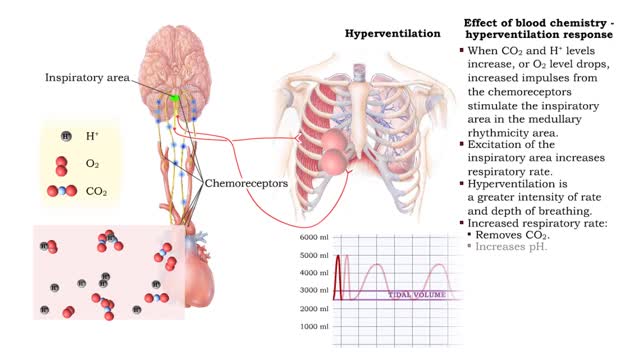
Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC, Views: 10701
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory r...
By: HWC, Views: 11845
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
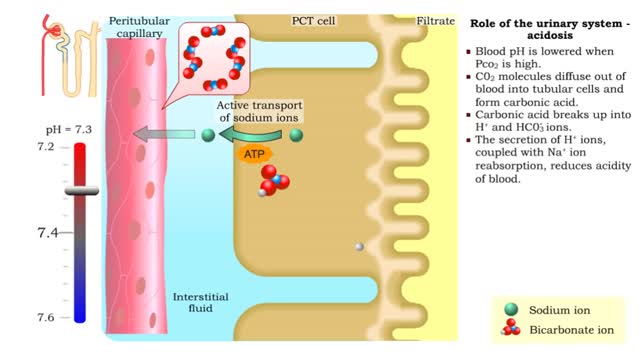
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11214
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
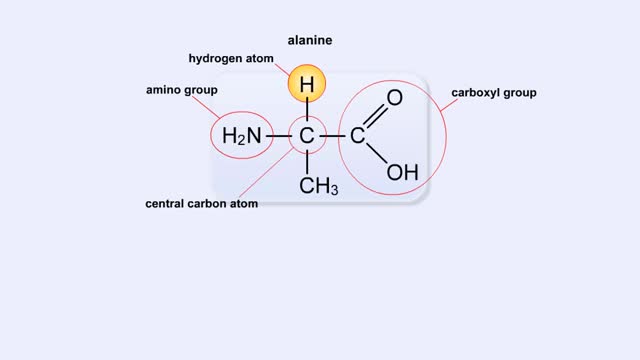
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 10671
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
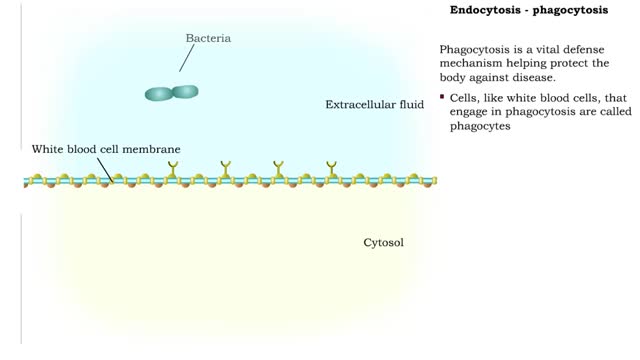
Endocytosis -Types and Phagocytosis
By: HWC, Views: 11126
Endocytosis is the process by which a substance is brought inside a cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. It is the opposite of endocytosis, the process by which substances exit the cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. Exocytosis – membrane-enclosed secret...
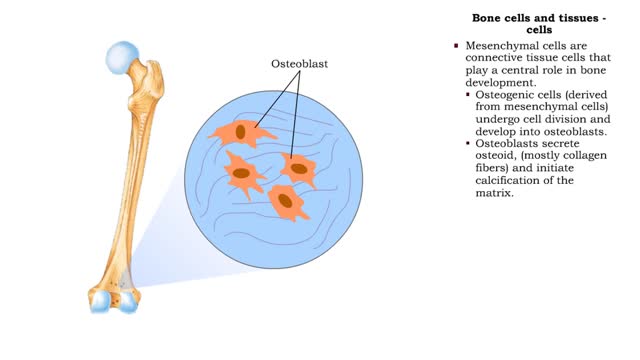
Bone cells and tissues - tissue composition and cells
By: HWC, Views: 11867
Bone tissue consists of bone cells secreting bone matrix. • The extracellular bone matrix is a connective tissue that is hard, yet flexible. • Collagen fibers provide flexibility. • Inorganic mineral salts (primarily calcium phosphate, or hydroxyapatite) provide hardness. • Togethe...
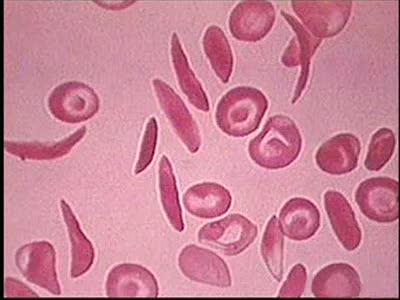
Introduction to Sickle Cell Anemia
By: Administrator, Views: 14582
Sickle cell anemia (sickle cell disease) is a disorder of the blood caused by an inherited abnormal hemoglobin (the oxygen-carrying protein within the red blood cells). The abnormal hemoglobin causes distorted (sickled appearing under a microscope) red blood cells.
Advertisement