Search Results
Results for: 'mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue'
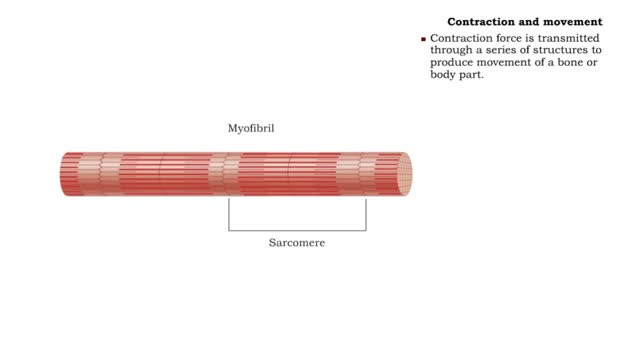
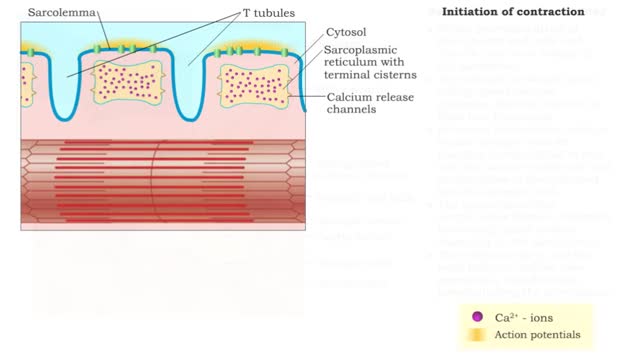
Contraction cycle of a sarcomere
By: HWC, Views: 11803
• A single nervous signal releases Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm and initiates the contraction cycle. step 1. ATP hydrolysis • ATP provides the to move myosin molecules back into the energized configuration necessary to perform the power stroke. Step 2. Crossbridge attachment • Myosin...
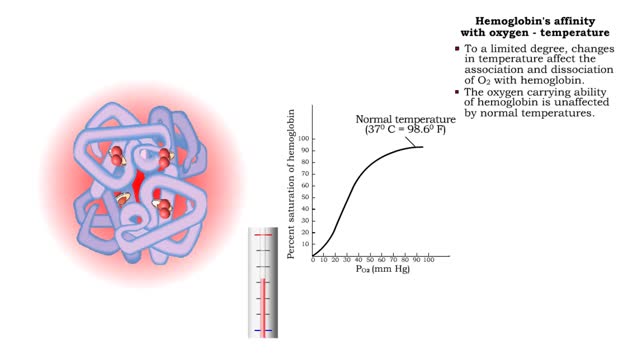
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 11299
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
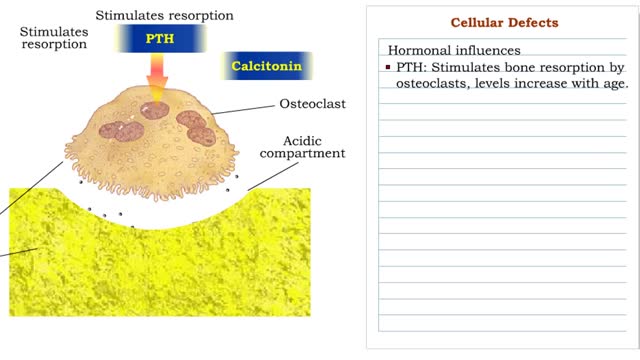
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 10972
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
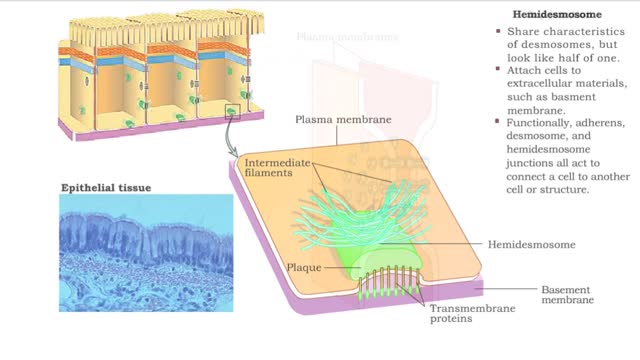
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 11666
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
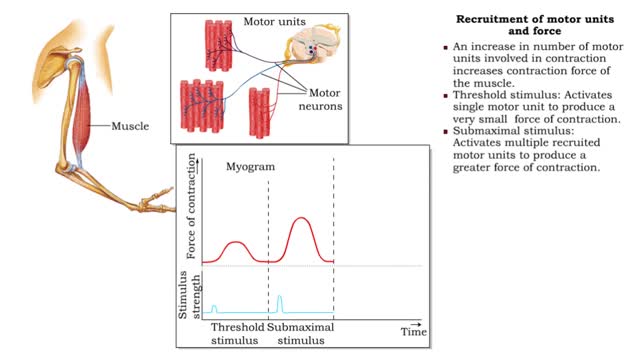
Frequency of stimulation and force (Recruitment of motor units and force)
By: HWC, Views: 11631
• Muscle tension depends on the frequency of stimulation. • Muscle twitch: First stimulus. • Wave summation: When a second stimulus excites a partially relaxed muscle, producing a stronger contraction. • Unfused tetanus: Successive stimulations at the same frequency, producing a se...
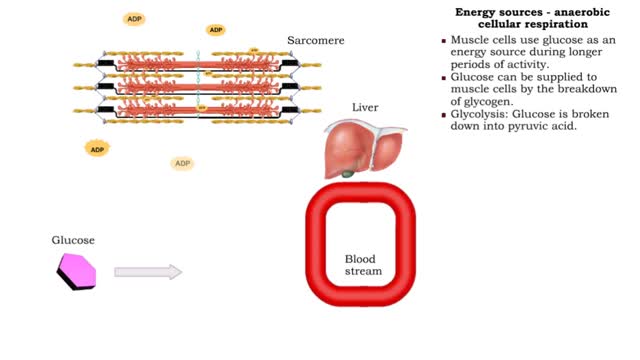
By: HWC, Views: 11540
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen syste...
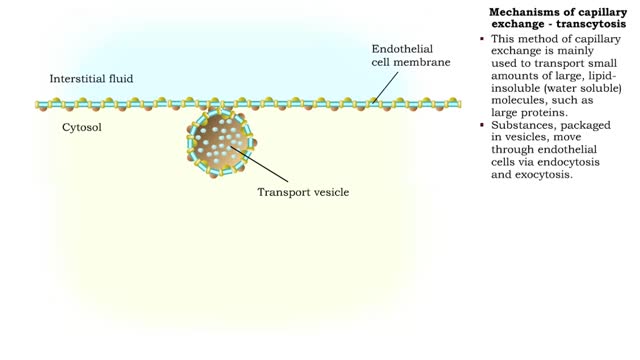
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11519
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
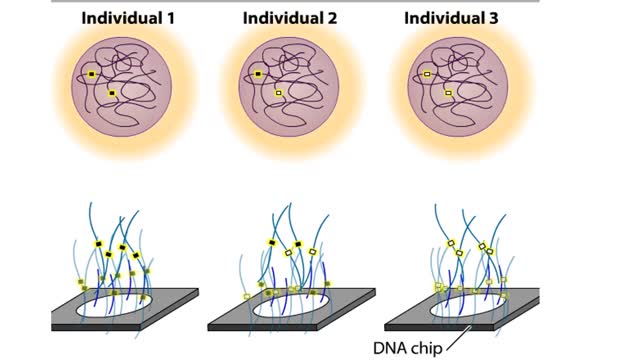
SNP Polymorphysim Microarray Chip - How to Test a Person's DNA
By: HWC, Views: 10680
To test a person's DNA, a researcher first needs a source of tissue. Most of the cells in a blood sample are red blood cells, which lack nuclei, but there are also a number of white blood cells, which do contain nuclei and chromosomal DNA. If we could see a particular DNA sequence in these cel...
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11821
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
Advertisement