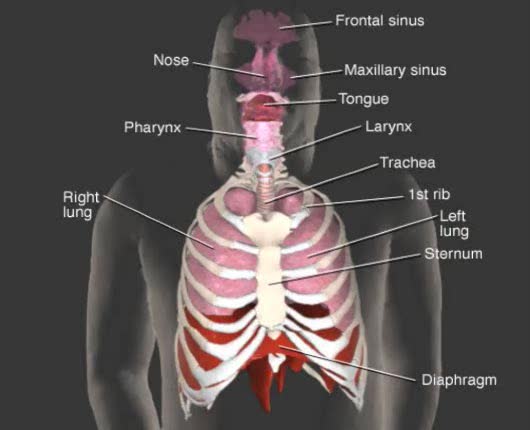
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/03/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC acidosis alkalosis homeostasis Chemical buffers The respiratory system urinary system Role of the respiratory system alveolar capillaries effect of altered ventilation rates
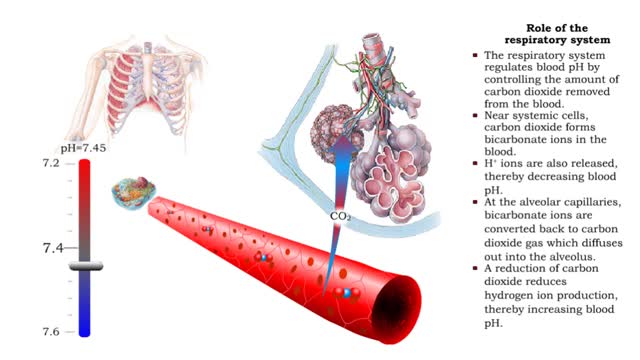
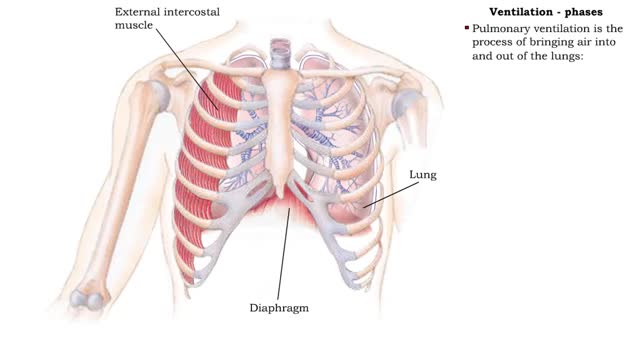
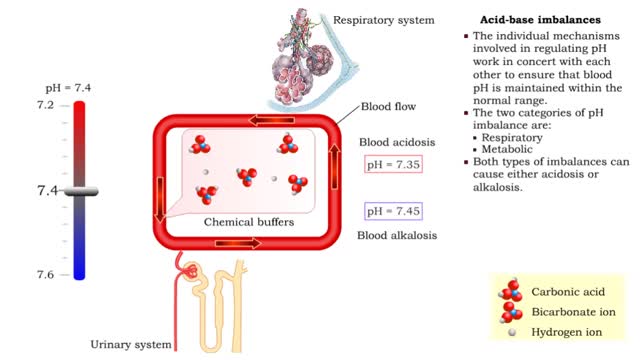
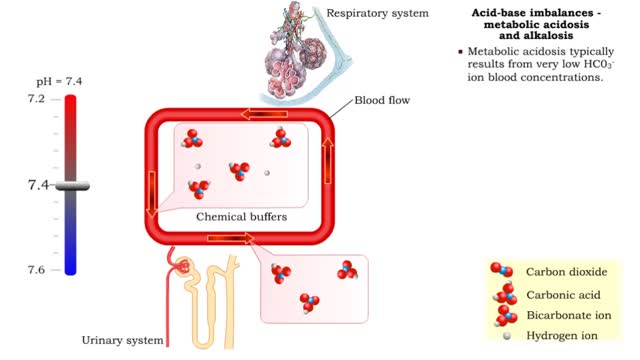
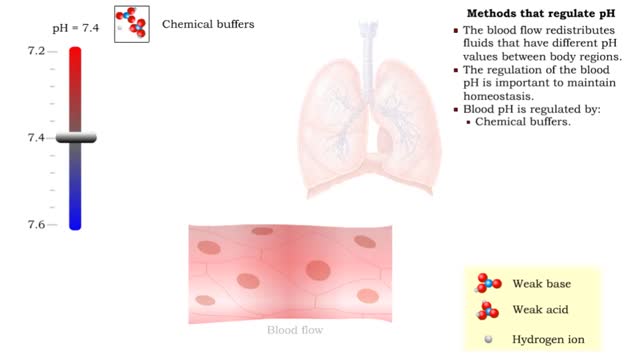
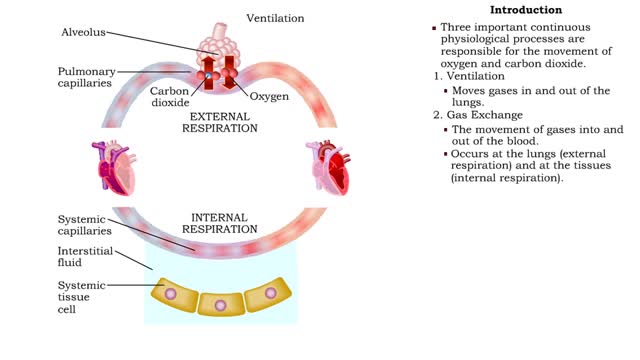
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, the pH value goes down resulting in a state of acidosis. • When hydrogen ion concentration decreases, the pH value goes up resulting in a state of alkalosis. • Life sustaining chemical reactions are catalyzed by enzymes which can only function effectively within narrow pH ranges. • The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All these methods may decrease or increase the pH value. • The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. • H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate ions are converted back to carbon dioxide gas which diffuses out into the alveolus. • A reduction of carbon dioxide reduces hydrogen ion production, thereby increasing blood pH. • Altered ventilation rates change the blood concentrations of CO2 and pH. • When blood Pco2 is low, and blood pH is high, the respiratory center decreases ventilation rate. • Less CO2 is removed from the blood and blood pH goes down. • When blood Pco2 is high, and blood pH is low, the respiratory center increases ventilation rate. • More CO2 is removed from the blood and blood pH goes up.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.