Net filtration pressure and lymph formation, edema & blood velocity
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 01/20/2020
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Bulk flow net filtration pressure capillary hydrostatic pressure colloidal osmotic pressure Blood velocity
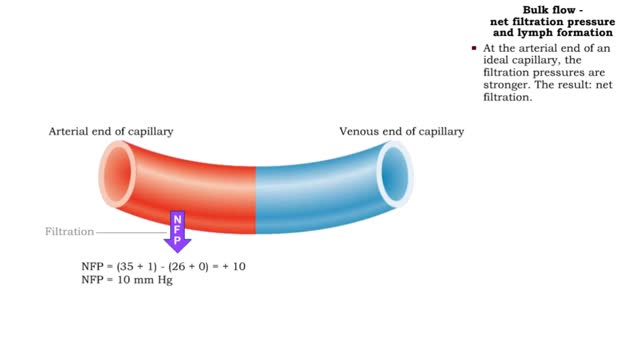
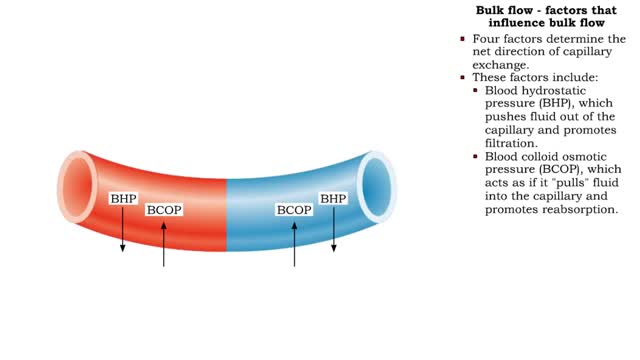
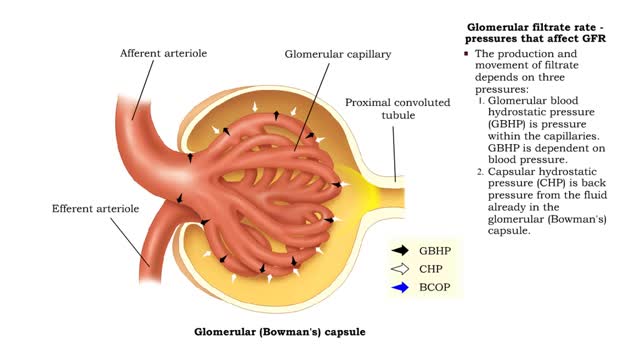
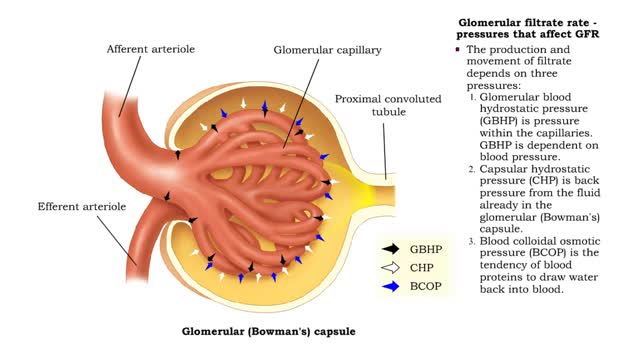
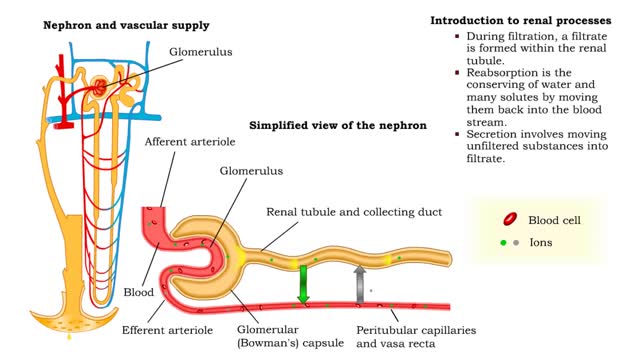
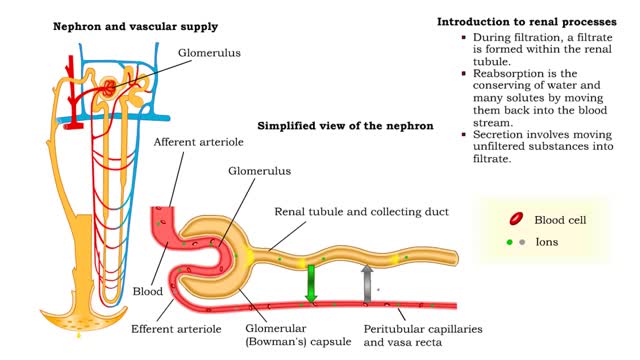
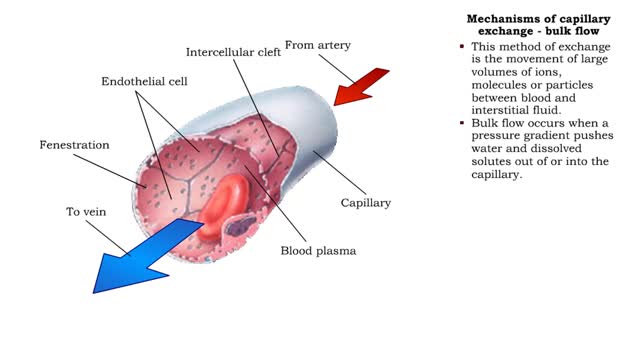
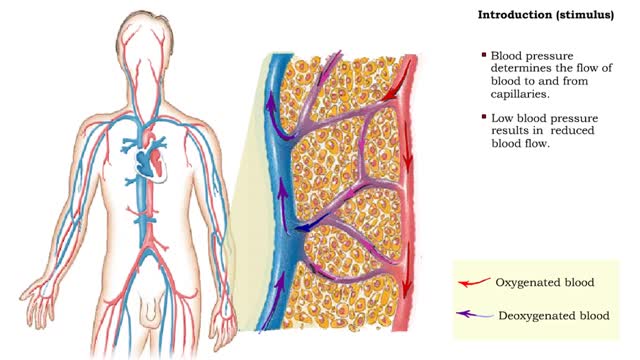
Bulk flow -net filtration pressure and lymph formation • The net filtration pressure (NFP) is the force promoting filtration minus the force promoting reabsorption. • At the arterial end of an ideal capillary, the filtration pressures are stronger. The result: net filtration. • At the venous end of an ideal capillary, the reabsorption pressures an stronger. The result: net reabsorption. • About 90% of the fluid that is filtered at the arterial end is reabsorbed at the venous end. • The remaining fluid drains. into lymphatic capillaries to form lymph. • An abnormal buildup of interstitial fluid results in swelling known as edema. • Major causes of edema include: • Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure • Increased capillary permeability • Decreased blood colloidal osmotic pressure • Blockage of lymphatic drainage • Blood velocity is inversely related to total cross-sectional area; the greater the area, the slower the velocity. • Capillaries have a higher total cross-sectional area; therefore blood flows more slowly. • Slower blood flow allows greater time for exchange of materials. • Arteries and veins have lower total cross-sectional areas; blood flows more quickly. • Blood velocity slows as blood travels away from heart, increases as it returns to heart.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement




Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.