Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 02/19/2020
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions Substrate Enzyme concentration zero order rate activation energy
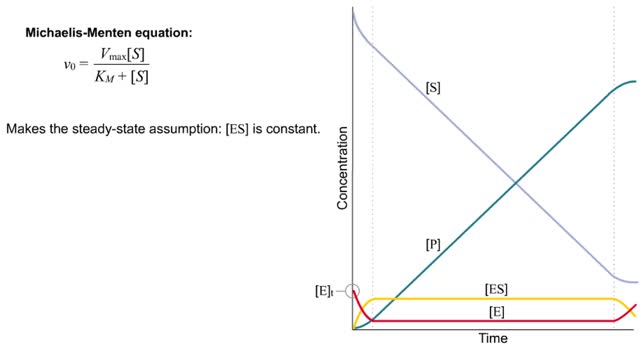
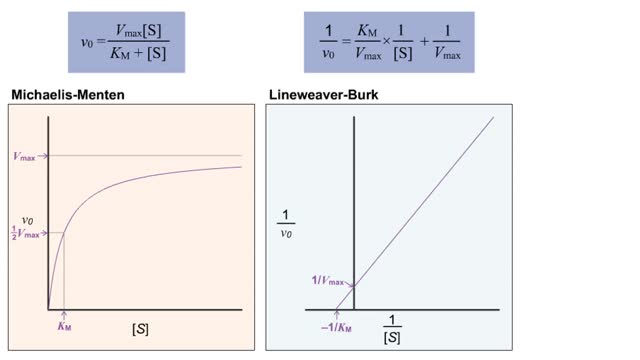
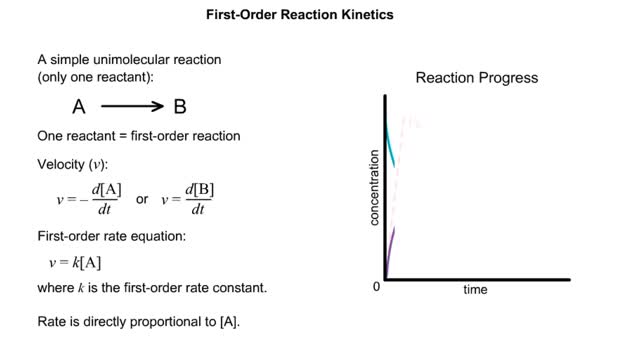
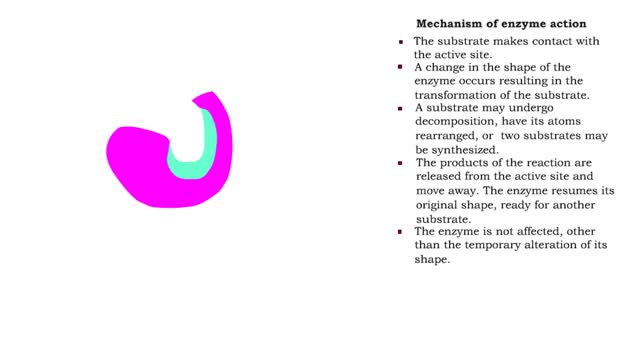
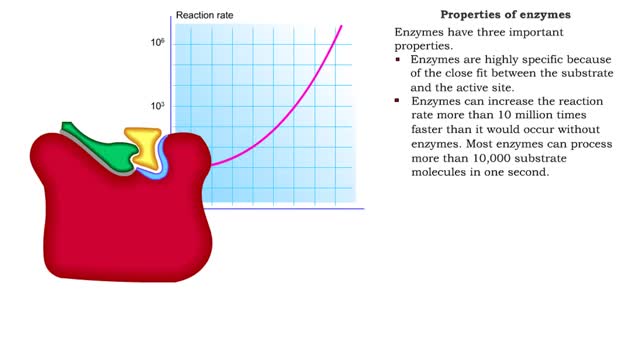
S P Substrate in great excess ([S] -- [E]) (More correctly [S] -- KM, but more on this later) Zero order rate equation: v = k where k is the zero-order rate constant (with respect to substrate). (More correctly [S] -- KM, but more on this later) Substrate forms complex with enzyme. Enzyme saturated with substrate = zero-order reaction. Enzyme concentration (availability) is rate limiting. V = Vmax Vmax is the enzyme-catalyzed zero order rate constant (with respect to substrate). Four Steps of Enzyme Action The enzyme and the substrate are in the same area. Some situations have more than one substrate molecule that the enzyme will change. The enzyme grabs on to the substrate at a special area called the active site. A process called catalysis happens. The enzyme releases the product
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement




Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.