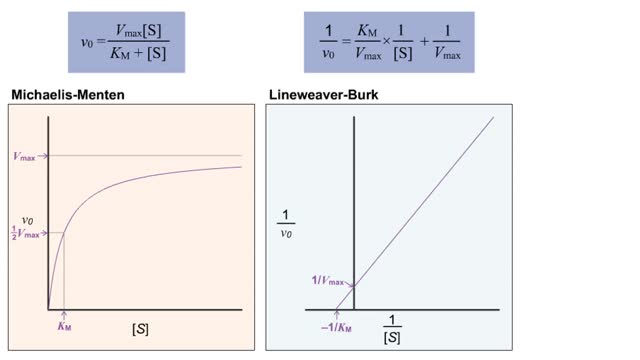
Michaelis–Menten equation & Kinetic parameters
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 02/19/2020
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Michaelis Menten equation Pre-Steady State enzyme Kinetic parameters reaction rate
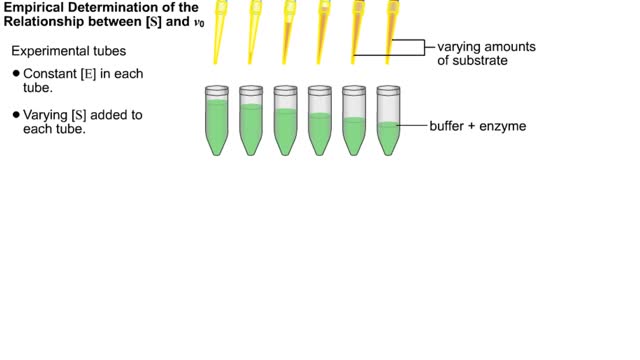
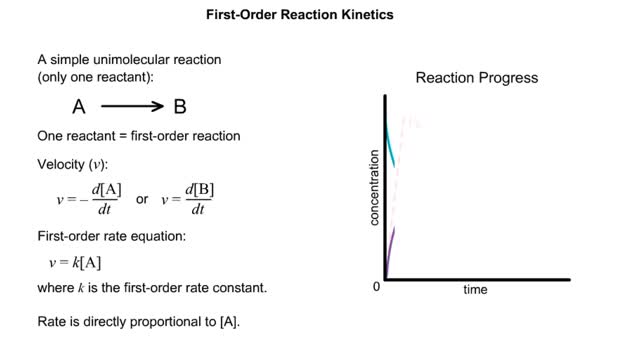
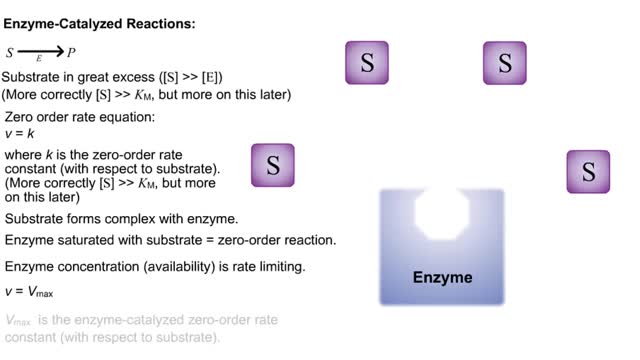
The Michaelis–Menten equation is the rate equation for a one-substrate enzyme-catalyzed reaction. This equation relates the initial reaction rate (v0), the maximum reaction rate (Vmax), and the initial substrate concentration [S] through the Michaelis constant KM—a measure of the substrate-binding affinity. When S is saturating, it is quickly bound by free enzyme to form ES complexes. During the steady state, the rate of decomposition of the ES complex equals its formation. Later, S becomes exhausted and its concentration nears the total enzyme concentration: less substrate is available to the enzyme, and the fraction of total enzyme in a complex with substrate begins to decrease. Note that E is the unbound enzyme concentration, not the total concentration of enzyme: [E] + [ES] Pre-Steady State In the short time prior to the steady state, there is a burst of ES complex formation as substrate is quickly bound by empty enzyme. The sub-maximal rate of substrate utilization and product formation reflects the fact that it takes some time for the ES complexes to form. When S is saturating, it is quickly bound by free enzyme to form ES complexes. During the steady state, the rate of decomposition of the ES complex equals its formation. Later, S becomes exhausted and its concentration nears the total enzyme concentration: less substrate is available to the enzyme, and the fraction of total enzyme in a complex with substrate begins to decrease Note that E is the unbound enzyme concentration, not the total concentration of enzyme: [E], = [E] + (ES] Initially, the concentration of product increases slowly because the enzymes must first bind substrate before reacting. During the steady state S is saturating and the rate of product formation becomes constant (zero order with respect to S). Finally, as IS] nears [E]l, the rate of the reaction (product formation) slows over time, similar to a first-order reaction where S is in short supply. Kinetic parameters are parameters included in the reaction rate equations, such as adsorption equilibrium constants, rate constants, and reaction order.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement




Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.