Secondary and tertiary levels of protein structure Animation
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 09/19/2023
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC protein's tertiary structure alpha helix beta sheet secondary structure Amino acid hydrogen bonding protein structure animation Secondary and tertiary levels of protein structure Animation
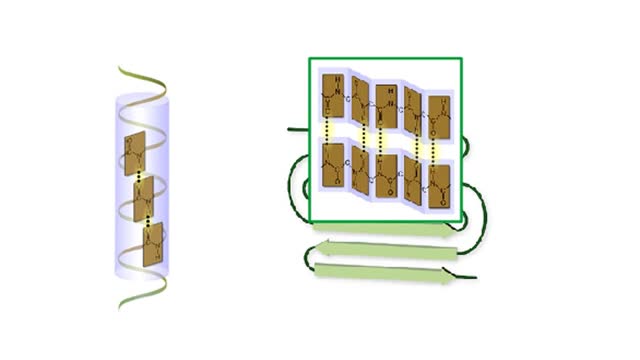
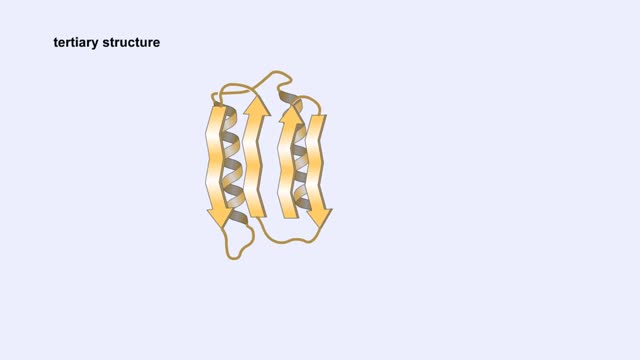
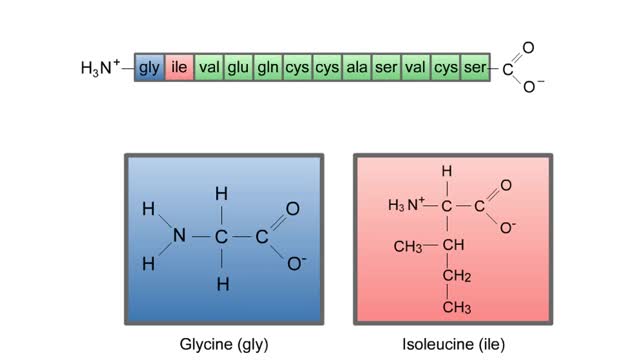
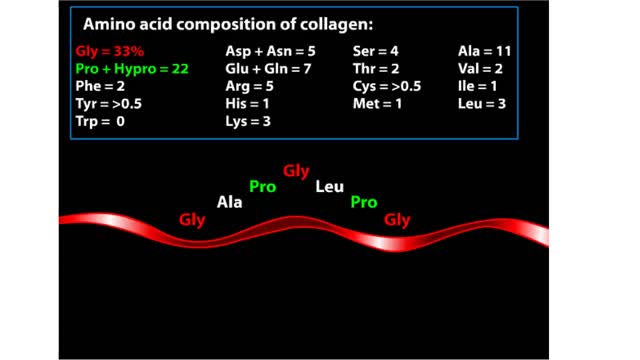
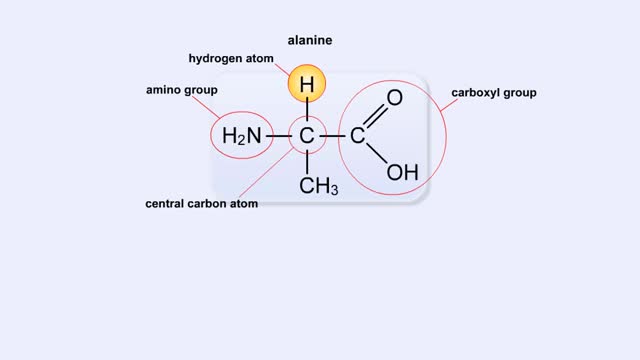
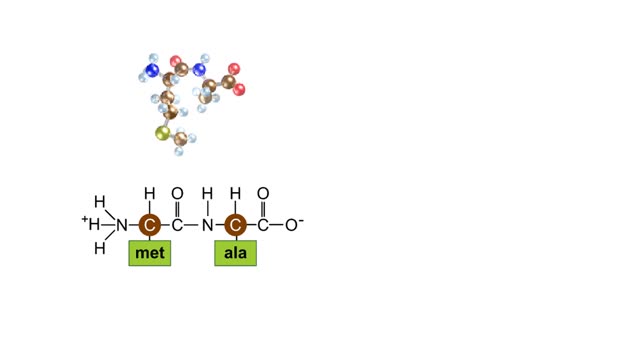
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like regions of a chain. This results in a beta sheet. The alpha helix and the beta sheet are the two most important types of secondary structure. Interactions among R groups cause adjacent coils or strands to fold up into one to dozens of compact domains. We call domain formation the protein's tertiary structure.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.