Search Results
Results for: 'pH'
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11129
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
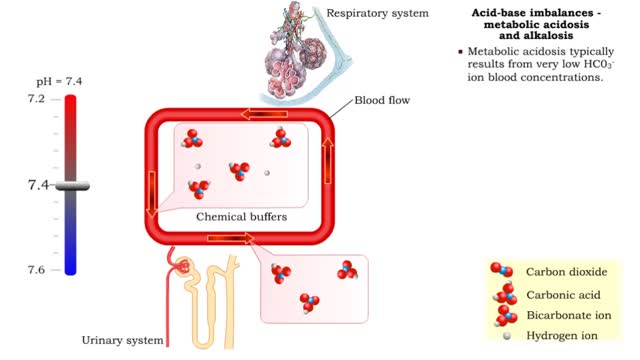
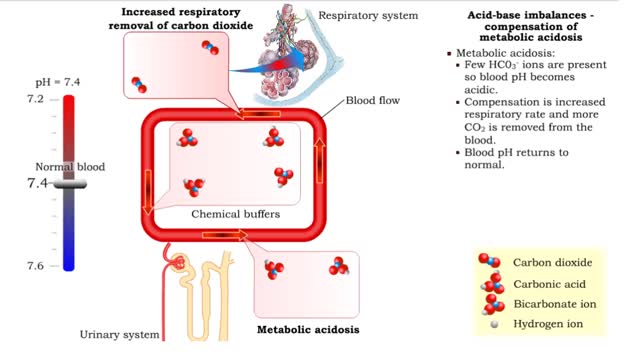
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11091
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
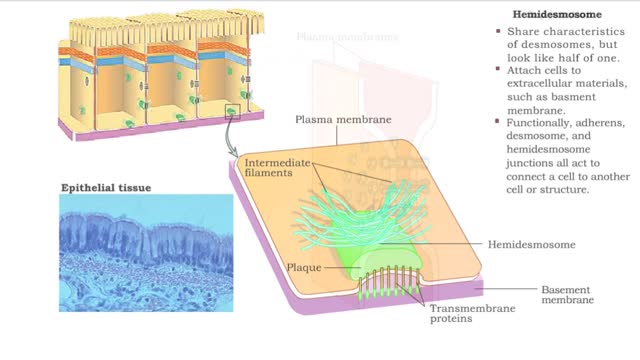
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 11253
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
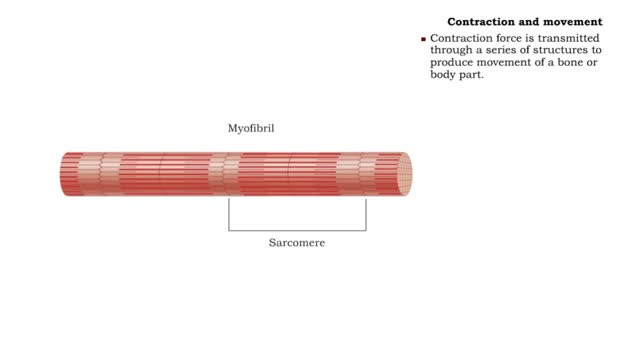
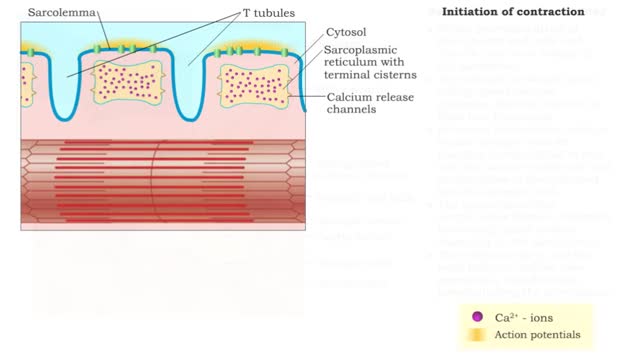
Contraction cycle of a sarcomere
By: HWC, Views: 11377
• A single nervous signal releases Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm and initiates the contraction cycle. step 1. ATP hydrolysis • ATP provides the to move myosin molecules back into the energized configuration necessary to perform the power stroke. Step 2. Crossbridge attachment • Myosin...
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11399
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
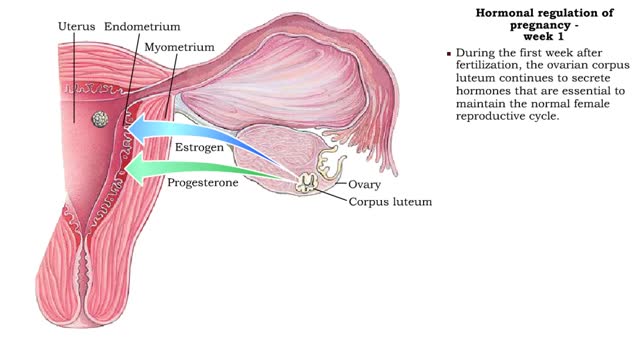
Hormonal regulation of pregnancy - week 1
By: HWC, Views: 11227
• During pregnancy, hormones play a significant role in triggering changes in the mother and fetus. • Ormones : • Maintain the lining of the uterus and prevent menstruation. Prepare the mammary glands for lactation. • Increase flexibility of the pubic symphysis. • Affect the mot...
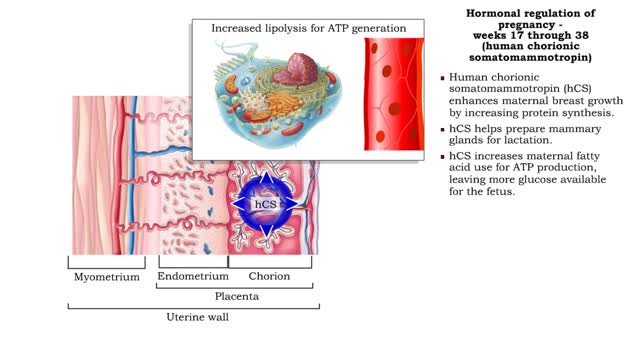
Hormonal regulation of pregnancy - weeks 17 through 38
By: HWC, Views: 11154
• Estrogens increase uterine blood flow, maintaining the endometrium during pregnancy. • High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit the synthesis of milk. Progesterone inhibits myometrial contractions of the uterus to prevent premature birth. • Relaxin inhibits myometrial contract...
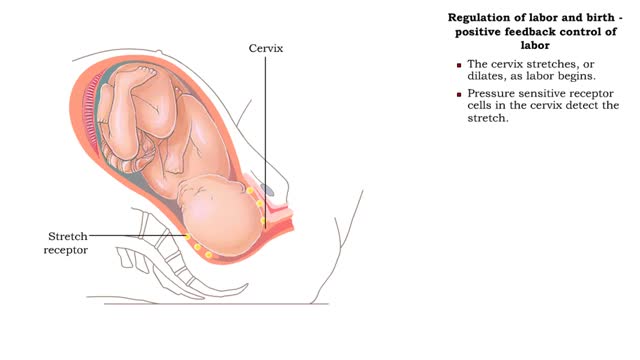
Labor and Childbirth - The Three Stages of Labor: Dilation, Expulsion & Placental مراحل الولادة
By: HWC, Views: 11324
Regulation of labor and birth - effects of estrogen and oxytocin on onset of labor • Just prior to birth, high placental corticotropin-releasing hormone levels stimulate the production of more estrogen. • High estrogen levels overcome the inhibitory effects of progesterone on uterine sm...
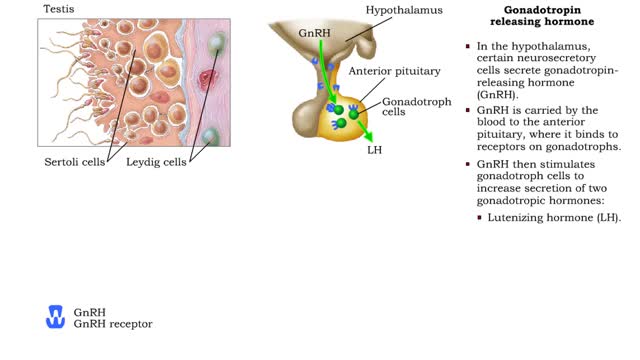
Male Reproductive System - The gonadotropin releasing hormone
By: HWC, Views: 11710
• Hormonal mechanisms that influence male reproductive function involve endocrine tissues contained in the: • Hypothalamus of the brain. • Anterior pituitary. • Testes. • In the hypothalamus, certain neurosecretory cells secrete gonadotropin- releasing hormone (GnRH). • GnRH ...
Advertisement