Search Results
Results for: 'glucose sugar'
By: HWC, Views: 10647
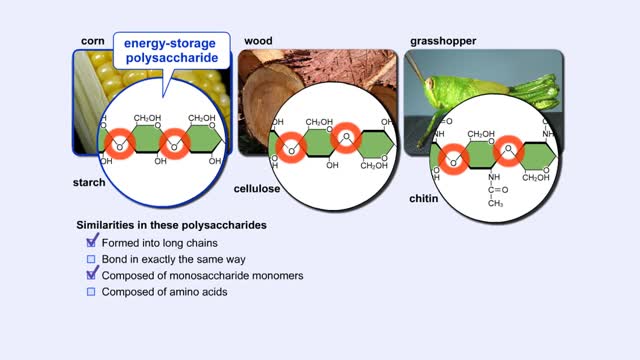
More complex sugars are called polysaccharides (from "poly" meaning "many" and "saccharum" meaning "sugar"). Many things in nature are made of polysaccharides. Here we show one of the polysaccharides in corn, another in wood, and another in the exoskeletons of insects like grasshoppers. How are a...
By: HWC, Views: 5247
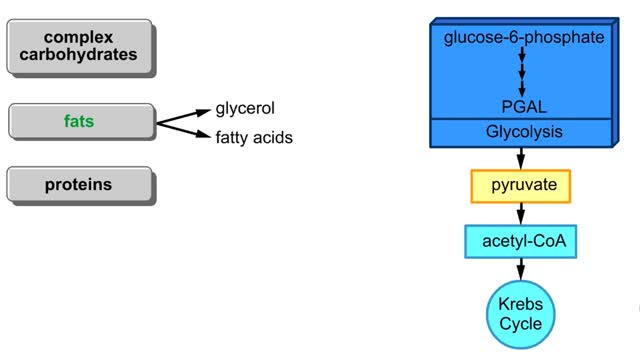
Points at which organic compounds enter the reaction stages of aerobic respiration. Complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose. They become the substrates for glycolysis. If your body doesn't need to burn glucose for energy, glucose-6-phosphate can be co...
By: Administrator, Views: 15298
The islets of Langerhans are composed of three major types of cells: Alpha cells secrete glucagon, elevating blood sugar. Beta cells secrete insulin, maintaining normal blood sugar. Delta cells secrete somatostatin, which suppresses release of glucagon and insulin. Hyposecretion or inadequa...
By: HWC, Views: 11364
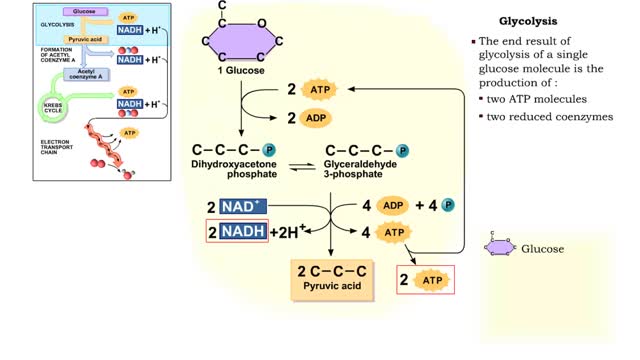
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Glycolysis - Introduction to ATP and the burning of sugar
By: HWC, Views: 11278
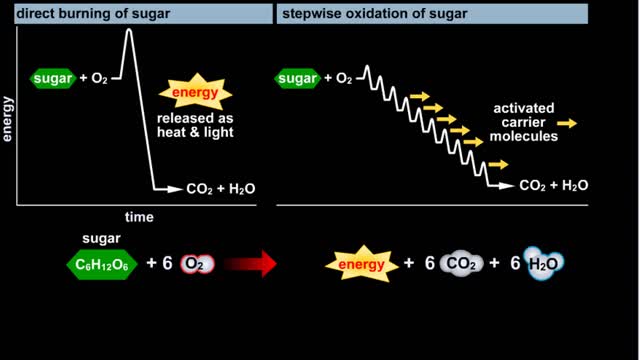
Do you use sugar with your coffee or tea? Or do you occasionally drink a sport or soft drink? As millions of people do each day, they obtain energy from the sugar added or contained in these drinks. How can we understand this concept of energy within a sugar molecule? Let's take a tablespoon ...
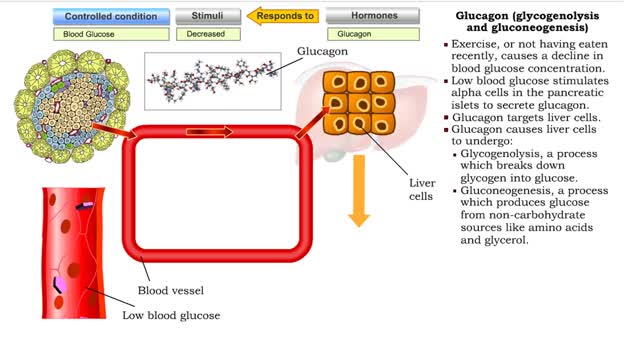
Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10820
• Exercise, or not having eaten recently, causes a decline in blood glucose concentration. • Low blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete glucagon. • Glucagon targets liver cells. • Glucagon causes liver cells to undergo: • Glycogenolysis, a proce...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10691
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
By: HWC, Views: 10866
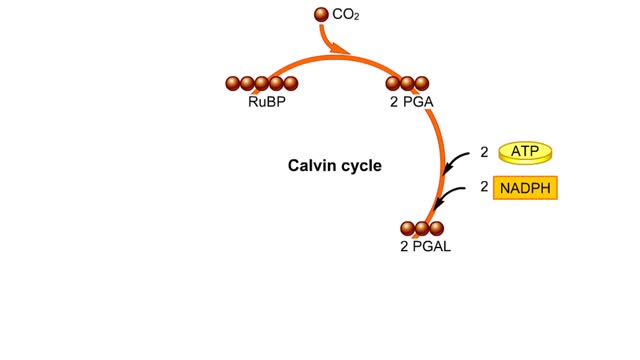
he light-independent reactions make sugars by way of a cyclic pathway called the Calvin cycle. The cycle begins when rubisco attaches a carbon from carbon dioxide to ribulose bisphosphate. The molecule that forms splits into two molecules of PGA. Each PGA gets a phosphate group from ATP a...
By: HWC, Views: 11260
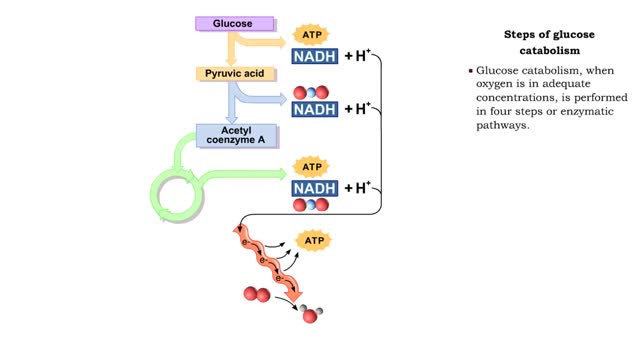
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
Advertisement