Search Results
Results for: 'Communication and regulation - body systems'
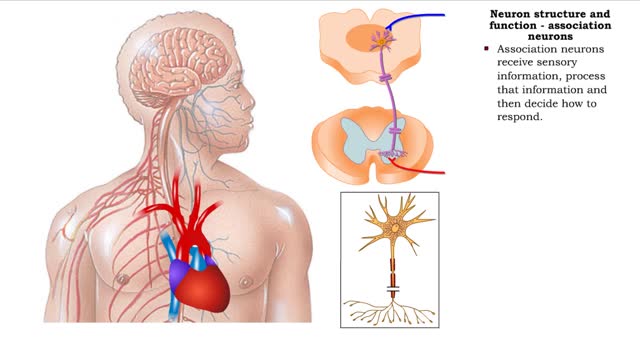
Neuron structure and function - sensory neurons, association neurons & motor neurons
By: HWC, Views: 11071
• The primary function of the nervous system is to provide rapid communication within the body to maintain homeostasis. • This function underlies behaviors, thinking and control of organ functions. • The basic functions of the nervous system are provided by: • Sensory neurons • ...
By: HWC, Views: 11205
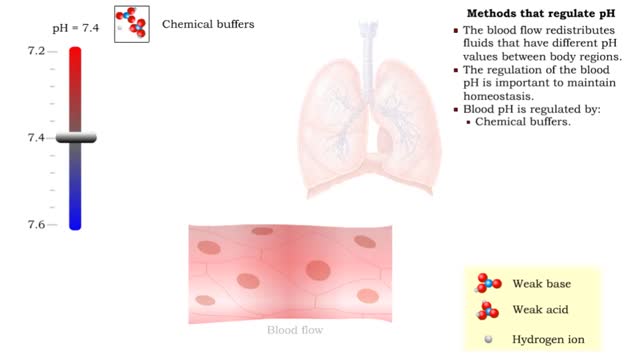
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
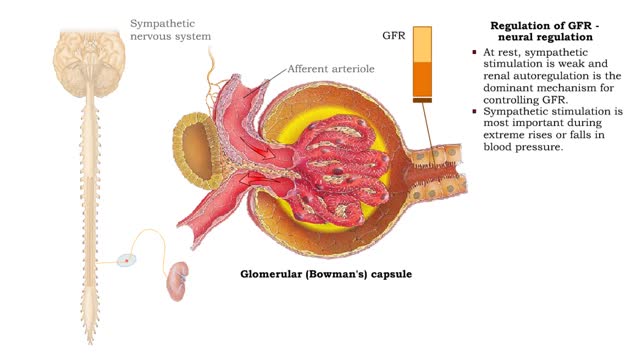
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12658
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
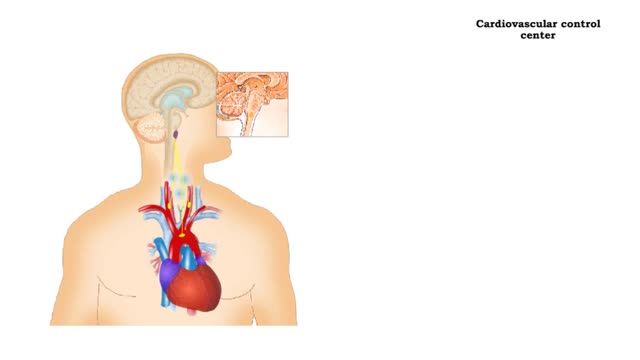
Negative Feedback Regulation of Blood Pressure
By: HWC, Views: 11082
stimulus • Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. Baroreceptors • The aortic arch carries blood to the body. • The common carotids ca...
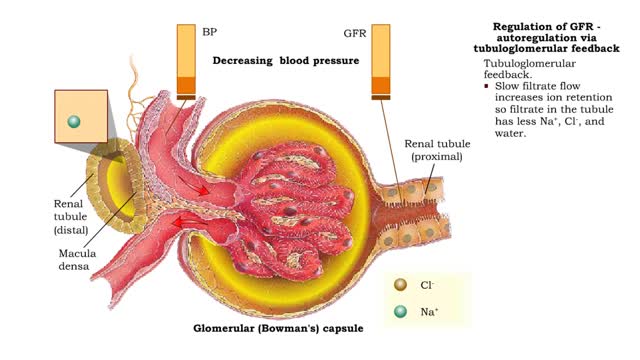
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12167
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
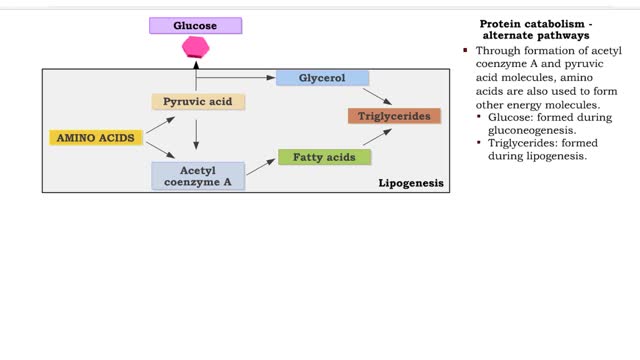
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11668
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
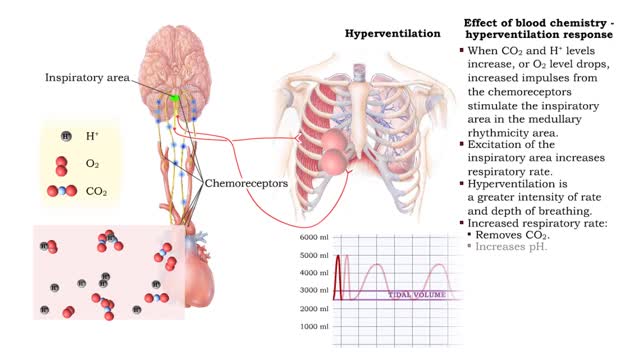
Effect of blood chemistry - stimuli, hyperventilation response and hypoventilation response
By: HWC, Views: 10725
• Respiratory rate is effected by changes in: • Blood pH. • Blood Pco2. • Blood P02. • Chemoreceptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems closely monitor the Fr, CO2 and 02 levels in blood. • Changes in frequency of impulses from Chemoreceptors affect respiratory r...
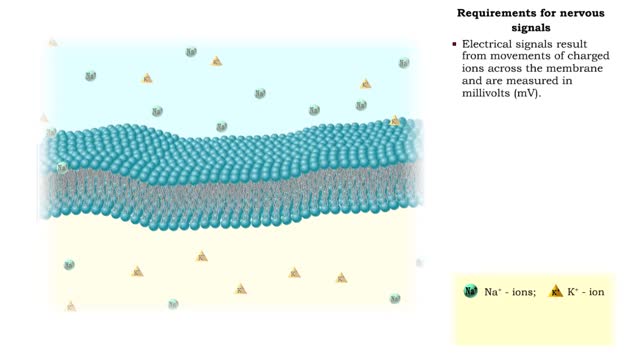
Requirements for nervous signals
By: HWC, Views: 11002
• The function of neurons is to allow communication between cells, thereby maintaining homeostasis. • Electrical signals, called membrane potentials, travel along the membranes of the neurons. • Voltage variability and distance traveled determine the type of nervous signal. 1. Graded...
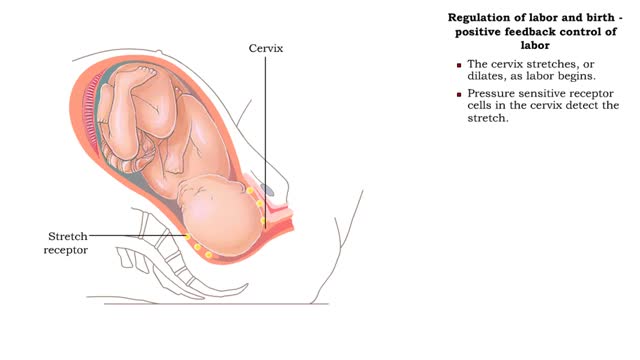
Labor and Childbirth - The Three Stages of Labor: Dilation, Expulsion & Placental مراحل الولادة
By: HWC, Views: 11506
Regulation of labor and birth - effects of estrogen and oxytocin on onset of labor • Just prior to birth, high placental corticotropin-releasing hormone levels stimulate the production of more estrogen. • High estrogen levels overcome the inhibitory effects of progesterone on uterine sm...
Advertisement