Search Results
Results for: 'oxidation reduction reaction'
By: HWC, Views: 10888
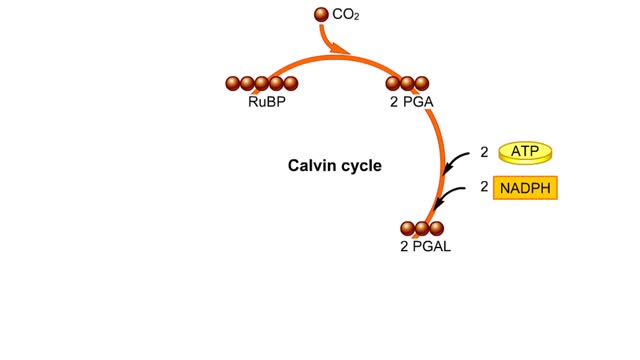
he light-independent reactions make sugars by way of a cyclic pathway called the Calvin cycle. The cycle begins when rubisco attaches a carbon from carbon dioxide to ribulose bisphosphate. The molecule that forms splits into two molecules of PGA. Each PGA gets a phosphate group from ATP a...
DNA Sequences - Dideoxy Sequencing
By: HWC, Views: 10432
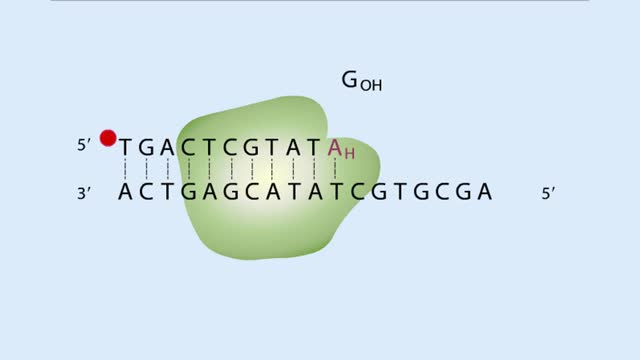
A short, radiolabeled primer is annealed to the single-stranded DNA to be sequenced. The DNA serves as a template for in vitro DNA synthesis. The DNA-primer mixture is split into four separate tubes. DNA polymerase and a solution of dNTPs are added to each tube. One of the four 2',3' dideoxy-N...
By: HWC, Views: 10873
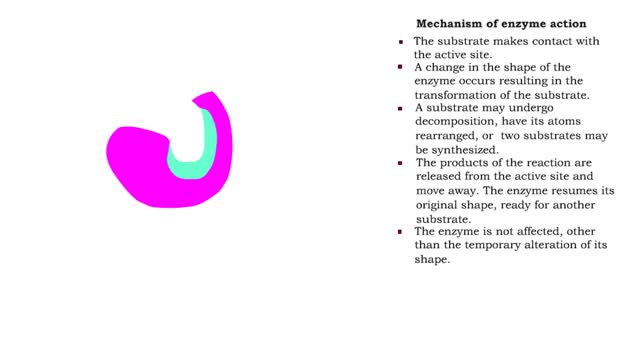
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 10084
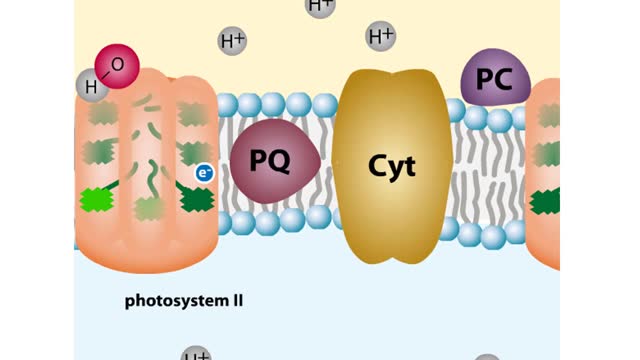
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
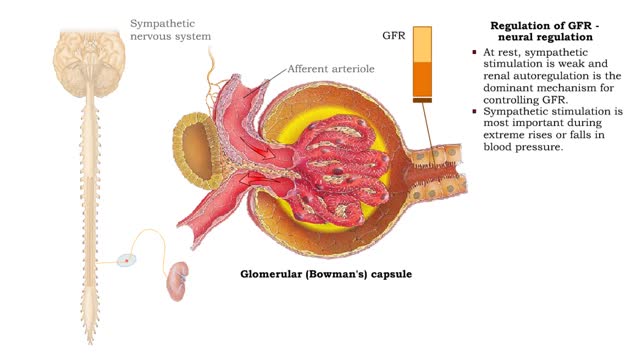
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12133
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
By: HWC, Views: 10711
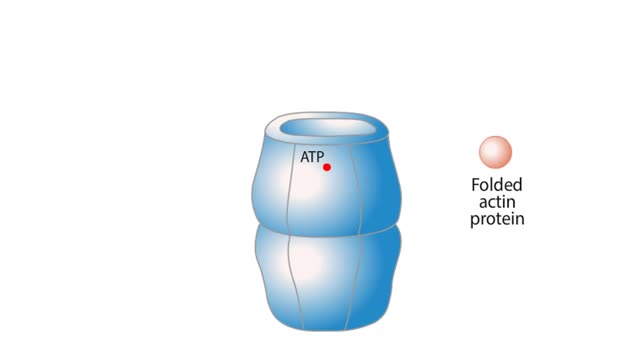
The life cycle of a typical protein begins with its synthesis on a ribosome. As the polypeptide chain grows, molecules of a chaperone protein bind along its length. This prevents misfolding of the nascent polypeptide. ATP binding causes chaperone release. For most proteins, the polypeptide th...
By: HWC, Views: 5285
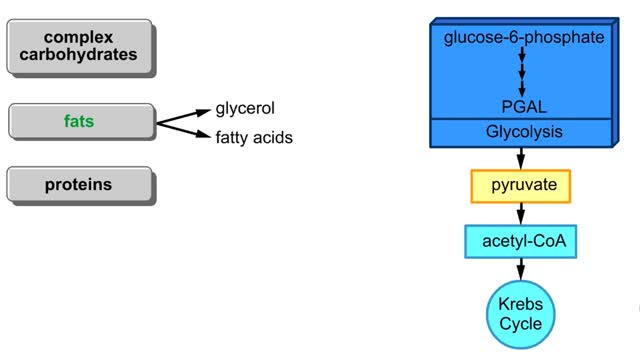
Points at which organic compounds enter the reaction stages of aerobic respiration. Complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose. They become the substrates for glycolysis. If your body doesn't need to burn glucose for energy, glucose-6-phosphate can be co...
Glycolysis - Introduction to ATP and the burning of sugar
By: HWC, Views: 11310
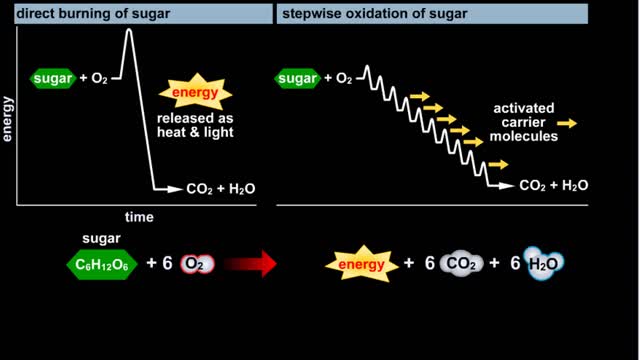
Do you use sugar with your coffee or tea? Or do you occasionally drink a sport or soft drink? As millions of people do each day, they obtain energy from the sugar added or contained in these drinks. How can we understand this concept of energy within a sugar molecule? Let's take a tablespoon ...
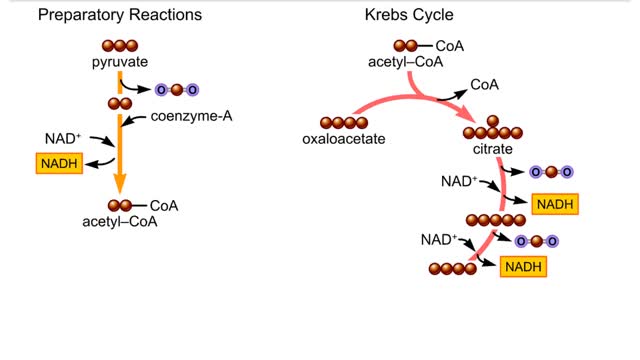
By: HWC, Views: 5288
The second-stage reactions of aerobic respiration. The second-stage reactions occur in a mitochondrion's inner compartment. In the first preparatory reaction, a carbon atom is stripped from pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide. The remaining carbons combine with coenzyme A and give ...
Advertisement