Search Results
Results for: 'The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H . • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • HC1 in gastric juice is important for the digestion of proteins. • HCl kills bacteria in food by destroying their proteins. Weak acids - role in the body ■ Carbonic acid is produced from CO2 and H2O. ■ H2CO3'
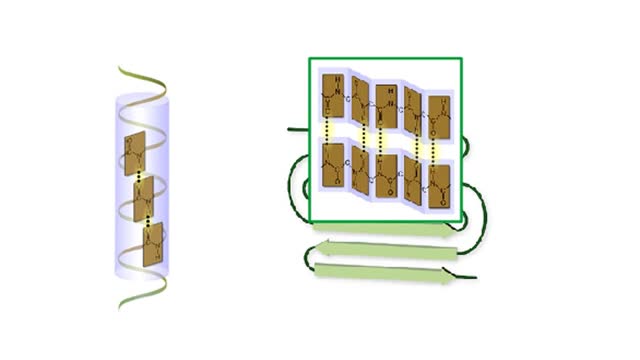
Protein Secondary and Tertiary Structures - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 2873
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like r...
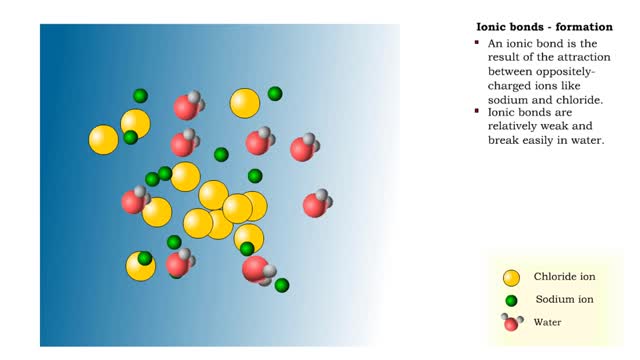
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 6883
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
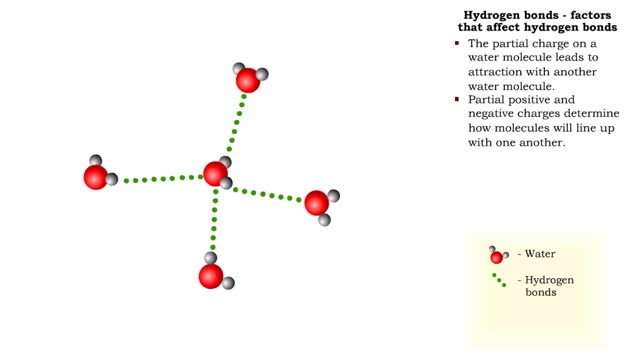
Hydrogen bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 7027
A hydrogen bond is the electromagnetic attraction between polar molecules in which hydrogen is bound to a larger atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This is not a sharing of electrons, as in a covalent bond. Instead, this is an attraction between the positive and negative poles of charged atoms. ...
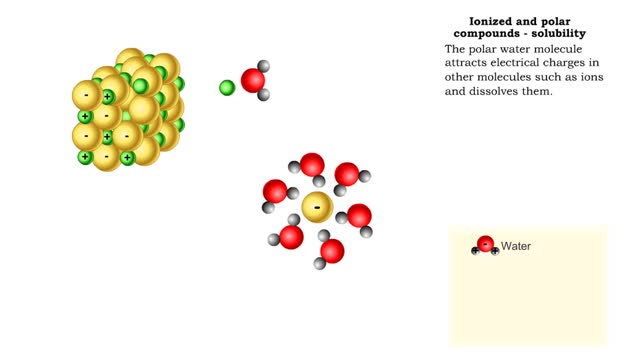
Properties of water -structure of water and polarity (Ionized and polar compounds)
By: HWC, Views: 6836
■ Water transports most of the molecules in the body. ■ The structure of a water molecule allows it to dissolve other molecules. ■ Shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen atom. ■ Oxygen end has a partial negative charge. ■ Hydrogen ends have a partial positive charge....
By: HWC, Views: 5964
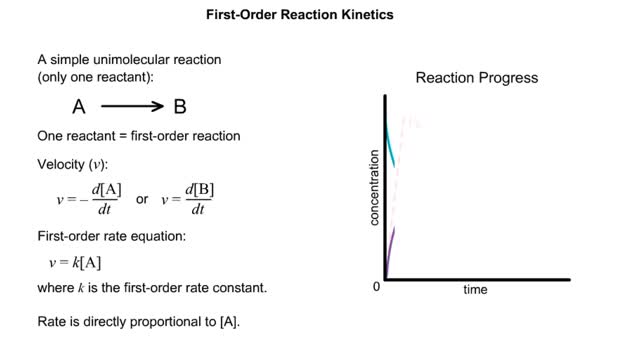
✔ https://HomeworkClinic.com ✔ https://Videos.HomeworkClinic.com ✔ Ask questions here: https://HomeworkClinic.com/Ask Follow us: ▶ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/HomeworkClinic ▶ Review Us: https://trustpilot.com/review/homeworkclinic.com Kinetics is the study of the rat...
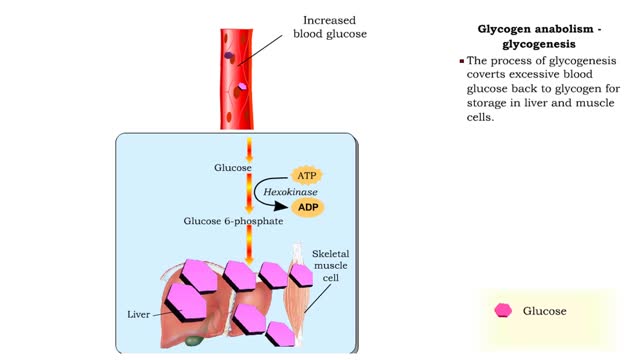
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 7018
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
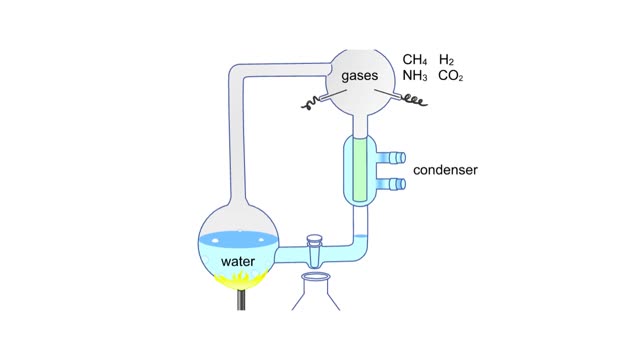
Miller's reaction chamber experiment Animation
By: HWC, Views: 292
A simple diagram of Stanley Miller and Harold Urey's experimental apparatus. The lower portion of the apparatus was filled with water. The upper portion was filled with a mixture of gases that simulated the earth's early atmosphere. Examples are methane, ammonia, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. ...
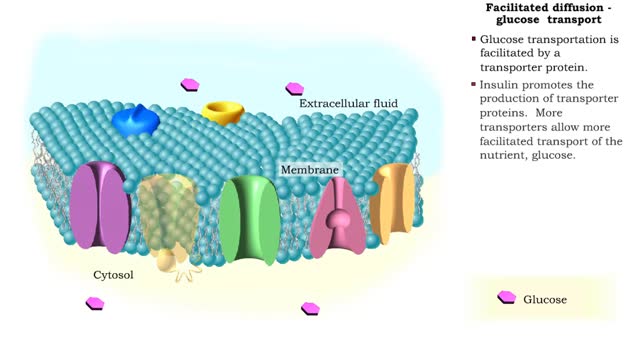
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 6921
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
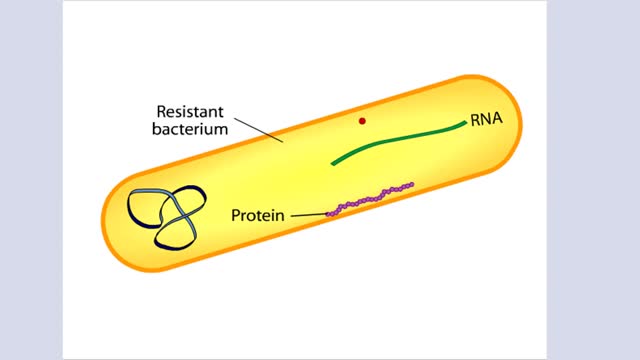
By: HWC, Views: 6355
The Crisis in Antibiotic Resistance More than 70 years ago, Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin. A few decades later, when this antibiotic was used in World War II, Fleming's discovery had revolutionized medicine. No longer did people have to die from something as trivial as an infected cut.Y...
Advertisement