Search Results
Results for: 'is a weak acid. • Few molecules dissociate because a strong attraction exists between H and HCO5. درجة الحموضة: ھو مقیاس لتحدید تركیز أیونات الھیدروجین H في المحلول یُرمز لدرجة الحموضة بالرمز (pH) وتُعرف أیضاً بالرقم الھیدروجیني أو الأس الهيدروجيني . درجة الحموضة مقیاس مدّرج من 0 إلى 14 ویُعبّر عن تركیز أیونات H وأیونات -OH في المحلول. فالمحالیل الحمضیة تمتلك قیمة pH أقل من (7)، وكلما قلت قیمة pH للحمض زادت قوتھ. والمحالیل القاعدیة تمتلك قیمة pH أكبر من (7)، وكلما زادت قیمة pH للقاعدة زادت قوتھا. أما الماء المقطر فتبلغ قیمة pH لھ (7)، أي أنھ یُعتبر متعادلاً وفق ھذا المقیاس لأن تركیز أیونات-OH مساٍو لتركیز أیونات H تعتمد قيمة PH للمحلول على تركيز كل من أيون الهيدروجين الموجب H وأيون الهيدروكسيد السالب OH-'
Molecules, Membrane Permeability and Structure
By: HWC, Views: 10399
Organisms are not isolated system at equilibrium and need to intake nutrients and electrolytes as remove wastes. Similarly Cells within an organism must also exchange compound by passing them through membrane. The permeability of a membrane is the rate of passive diffusion of molecules th...
By: HWC, Views: 4918
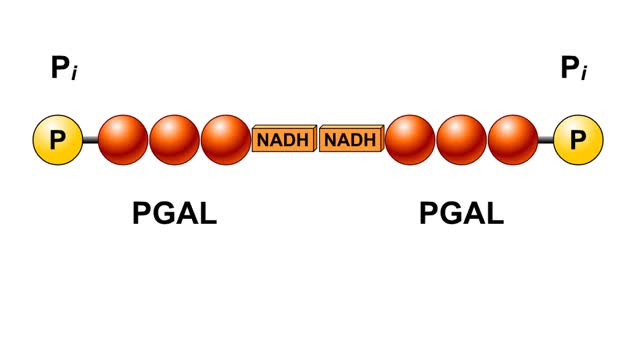
In glycolysis, a six-carbon glucose molecule is split into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules. In this animation, each carbon molecule is represented by a red ball. The end products of glycolysis are two molecules of pyruvate. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of ...
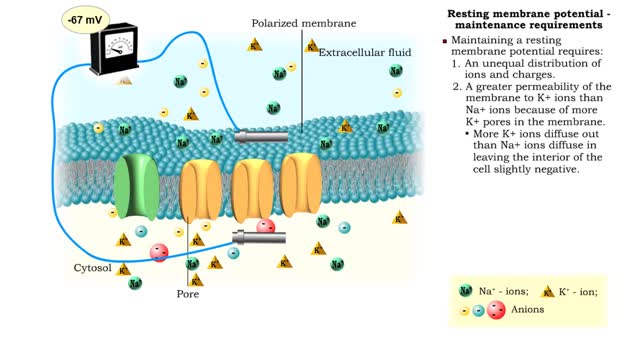
Resting membrane potential - electrical polarity and maintenance requirements
By: HWC, Views: 10586
• A resting membrane potential exists when there is a buildup of: 1. positive ions outside the membrane. 2. negative ions inside the membrane. • Membranes with opposing charges are said to be polarized. • The difference in charge applies only to the small distance across the membran...
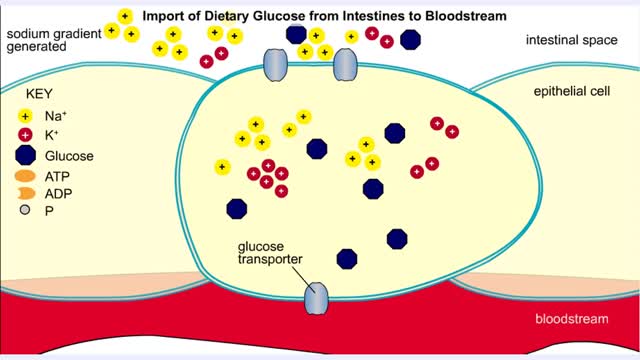
Import of Dietary Glucose from Intestines to Bloodstream
By: HWC, Views: 10334
• Membranes have hydrophobic interiors. which resist the passage of hydrophilic compounds and ions. • However. transporter membrane proteins facilitate the passage of these molecules. • Passive transporters accelerate diffusion of molecules towards equilibrium (decrease a concentrat...
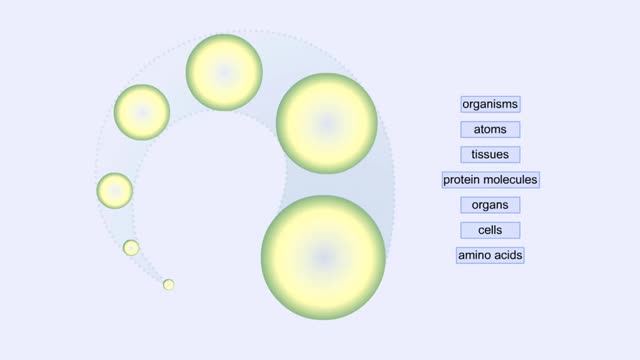
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 10406
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
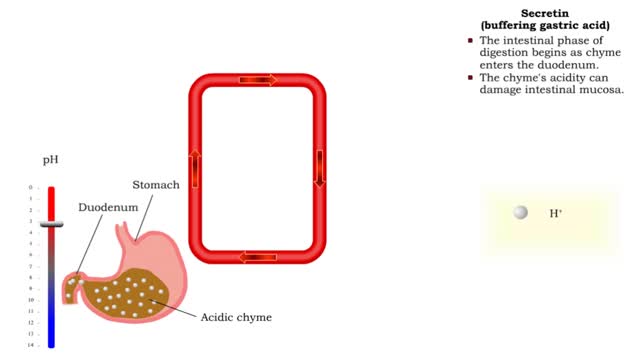
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 10485
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
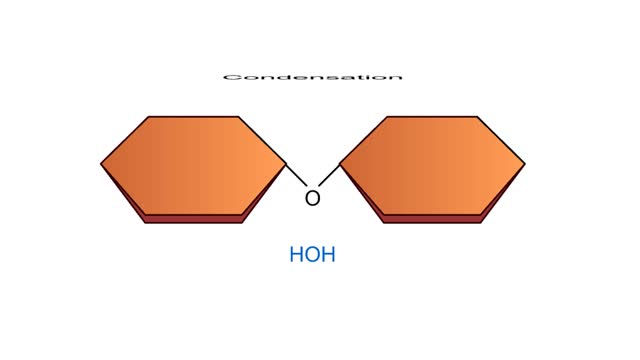
Condensation and Hydrolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4736
A condensation reaction joins two molecules together to form one larger molecule. An enzyme removes a hydroxyl group from one molecule and a hydrogen atom from another, then speeds the formation of a bond between the two molecules at their exposed sites. Typically the discarded atoms join t...
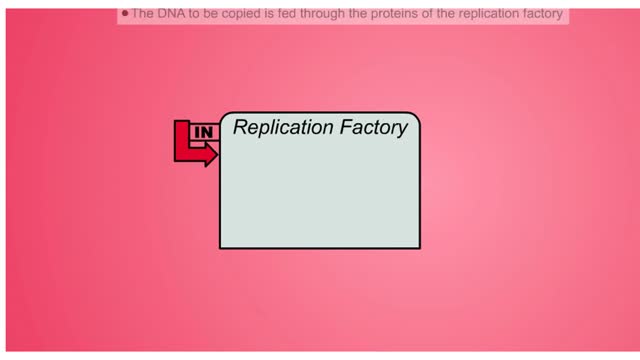
DNA Replication Factory and Protein
By: HWC, Views: 10512
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) carries all the genetic information needed to re-create itself and to pass on the characteristics of the organism. The “factory” model of DNA replication hypothesizes a specific nuclear structure in which the molecular machinery for replication forks are brou...
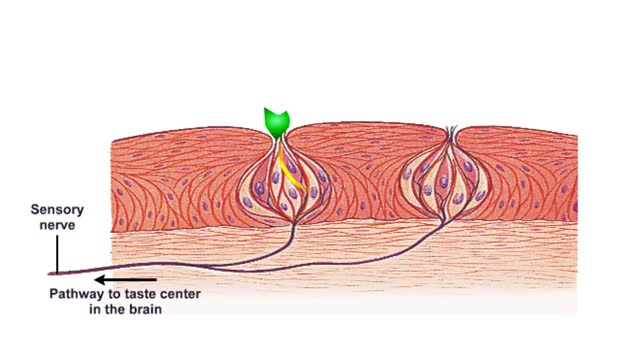
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7821
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
Advertisement