Search Results
Results for: 'is a weak acid. • Few molecules dissociate because a strong attraction exists between H and HCO5. درجة الحموضة: ھو مقیاس لتحدید تركیز أیونات الھیدروجین H في المحلول یُرمز لدرجة الحموضة بالرمز (pH) وتُعرف أیضاً بالرقم الھیدروجیني أو الأس الهيدروجيني . درجة الحموضة مقیاس مدّرج من 0 إلى 14 ویُعبّر عن تركیز أیونات H وأیونات -OH في المحلول. فالمحالیل الحمضیة تمتلك قیمة pH أقل من (7)، وكلما قلت قیمة pH للحمض زادت قوتھ. والمحالیل القاعدیة تمتلك قیمة pH أكبر من (7)، وكلما زادت قیمة pH للقاعدة زادت قوتھا. أما الماء المقطر فتبلغ قیمة pH لھ (7)، أي أنھ یُعتبر متعادلاً وفق ھذا المقیاس لأن تركیز أیونات-OH مساٍو لتركیز أیونات H تعتمد قيمة PH للمحلول على تركيز كل من أيون الهيدروجين الموجب H وأيون الهيدروكسيد السالب OH-'
By: HWC, Views: 10385
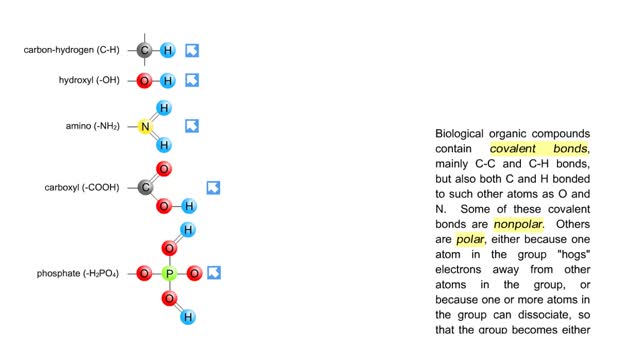
Biological organic compounds contain covalent bonds, mainly C-C and C-H bonds, but also both C and H bonded to such other atoms as O and N. Some of these covalent bonds are nonpolar. Others are polar, either because one atom in the group "hogs" electrons away from other atoms in the group, or...
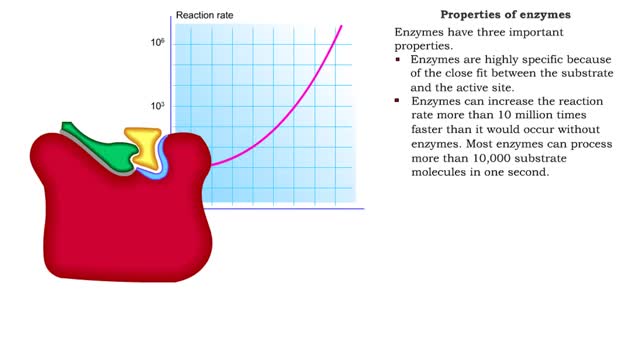
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 10839
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
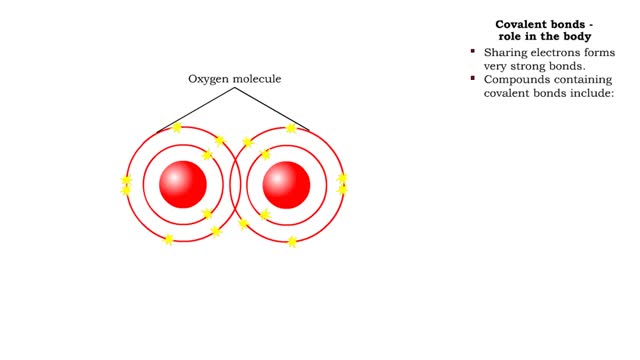
Covalent bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 10828
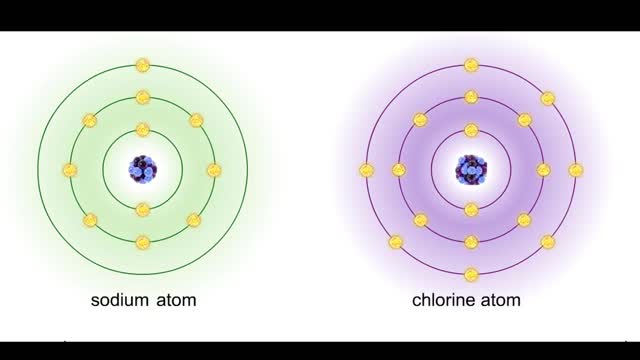
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This is opposed to an ionic bond, where electrons are actually transferred from one atom to another. Formation • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by sharing electrons. • Two oxygen atoms sharing electrons form on...
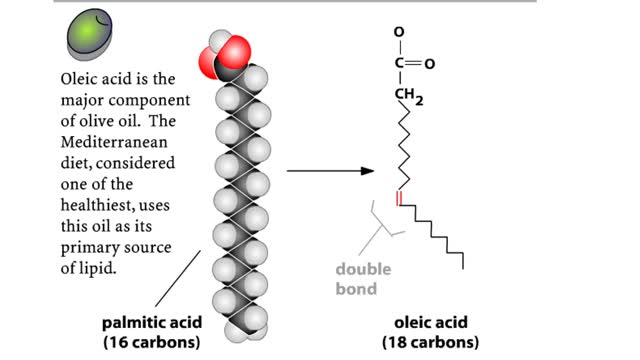
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Lipids
By: HWC, Views: 10271
A triglyceride (also called triacylglycerol) is composed of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. The fatty acids attach to the glycerol molecule by a covalent ester bond. The long hydrocarbon chain of each fatty acid makes the triglyceride molecule nonpolar and hydrophobic. Pa...
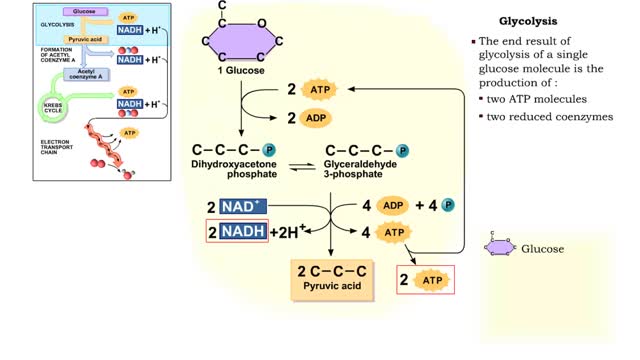
By: HWC, Views: 11209
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10622
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
By: HWC, Views: 9666
The slight positive charge of a hydrogen atom in a water molecule can attract an atom with a slight negative charge, such as the nitrogen in a molecule of ammonia. This forms a hydrogen bond between the two atoms. Hydrogen bonds join the two strands of a DNA molecule. Although hydrogen bo...
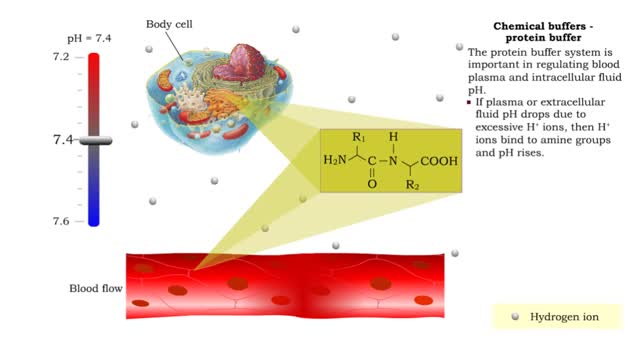
Chemical Buffers - protein buffer, phosphate buffer system and bicarbonate buffer system
By: HWC, Views: 11051
• There are a variety of chemicals in body fluids that prevent the fluids from undergoing large changes in. • These chemicals buffer or regulate fluctuations in H+ concentration. • Chemical buffers: • Bind to H+ ions when there are too many in a solution so pH remains normal. •...
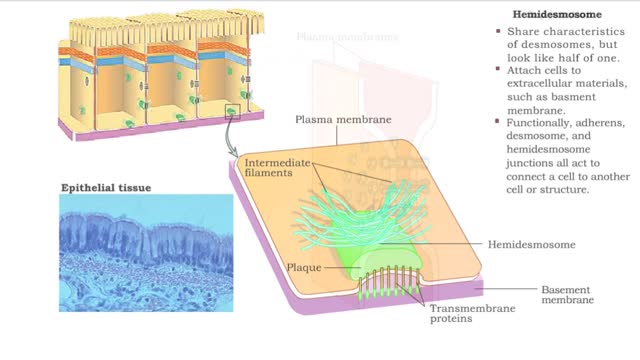
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 11235
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
Advertisement