Search Results
Results for: 'is a weak acid. • Few molecules dissociate because a strong attraction exists between H and HCO5. درجة الحموضة: ھو مقیاس لتحدید تركیز أیونات الھیدروجین H في المحلول یُرمز لدرجة الحموضة بالرمز (pH) وتُعرف أیضاً بالرقم الھیدروجیني أو الأس الهيدروجيني . درجة الحموضة مقیاس مدّرج من 0 إلى 14 ویُعبّر عن تركیز أیونات H وأیونات -OH في المحلول. فالمحالیل الحمضیة تمتلك قیمة pH أقل من (7)، وكلما قلت قیمة pH للحمض زادت قوتھ. والمحالیل القاعدیة تمتلك قیمة pH أكبر من (7)، وكلما زادت قیمة pH للقاعدة زادت قوتھا. أما الماء المقطر فتبلغ قیمة pH لھ (7)، أي أنھ یُعتبر متعادلاً وفق ھذا المقیاس لأن تركیز أیونات-OH مساٍو لتركیز أیونات H تعتمد قيمة PH للمحلول على تركيز كل من أيون الهيدروجين الموجب H وأيون الهيدروكسيد السالب OH-'
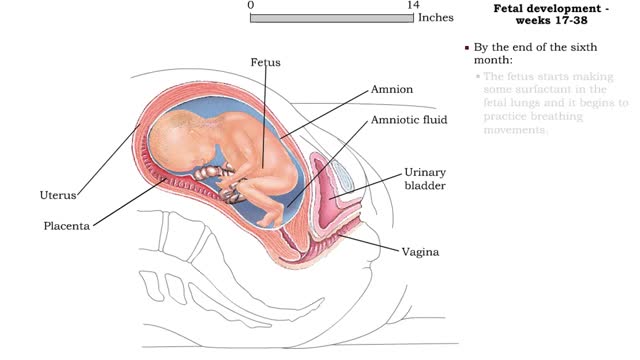
Fetal development - Weeks 9 to 38
By: HWC, Views: 6771
Weeks 9-12 • Fetal development during the third month includes: • A large head, about 1/2 the length of the fetus. • Visible eyes and ears. • A detectable heartbeat. • Kidneys that form urine. • Gender identification. • Weak, undetectable body movements. • By the e...
By: HWC, Views: 860
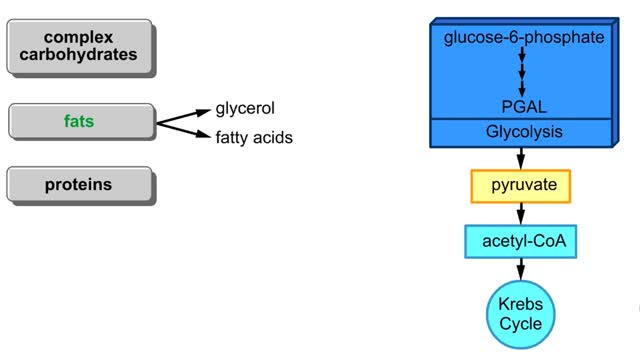
Points at which organic compounds enter the reaction stages of aerobic respiration. Complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose. They become the substrates for glycolysis. If your body doesn't need to burn glucose for energy, glucose-6-phosphate can be co...
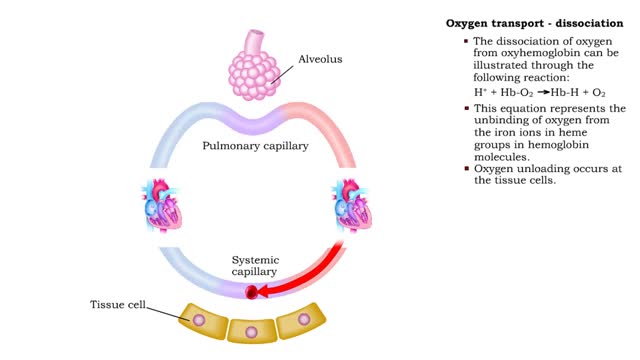
Oxygen transport: association and dissociation & Factors that affect hemoglobin's saturation with O2
By: HWC, Views: 6618
• The production of oxyhemoglobin can be illustrated through the following reaction: 02 + Hb-H --) Hb-02 + H+ • This equation represents the binding of oxygen to the iron ions in heme groups in hemoglobin molecules. • Oxygen binding or loading occurs at the lungs • The dissociatio...
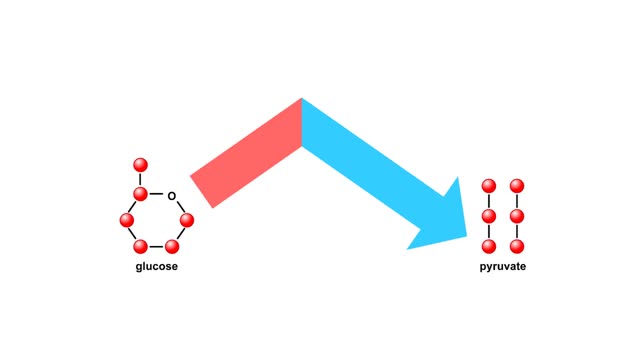
Energy inputs and release in glycolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 609
Glycolysis breaks the six-carbon sugar glucose into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. The first steps of glycolysis require an energy input in the form of two phosphate-group transfers from ATP. These phosphorylations raise the energy level of glucose enough to allow the energy-releas...
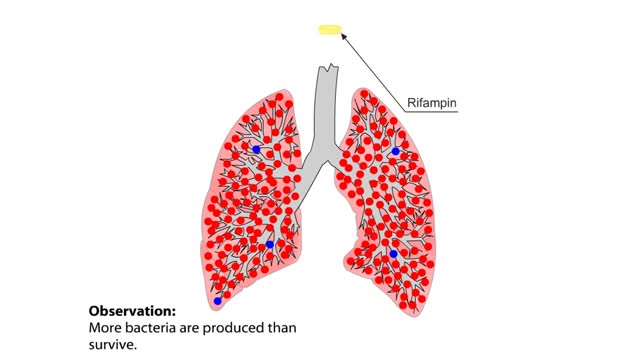
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Drug Resistance and Natural Selection
By: HWC, Views: 5451
The evolution of drug resistance in microorganisms, such as M. tuberculosis, that cause human diseases is of particular concern to biologists. When Mycobacterium tuberculosis infects the lungs of humans, it causes the disease tuberculosis, also called TB. Once infected, the lungs act as a new...
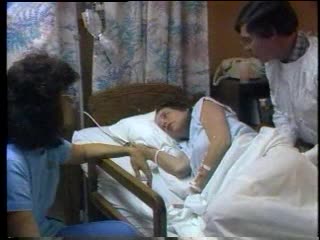
Labor and Delivery - Transition
By: Administrator, Views: 268
The last part of active labor – when your cervix dilates from 8 to a full 10 centimeters – is called the transition period because it marks the shift to the second stage of labor. This is the most intense part of labor. Contractions are usually very strong, coming every two and a half to t...
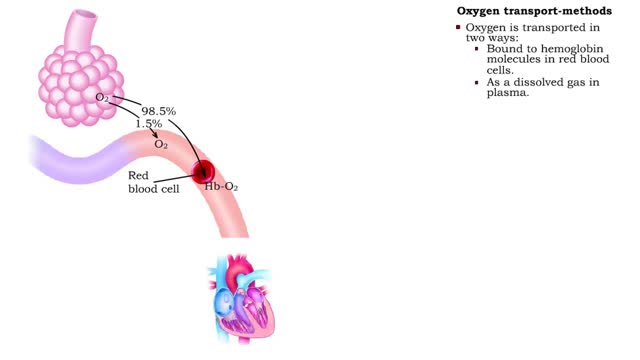
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 6447
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
By: HWC, Views: 6661
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
By: Administrator, Views: 9671
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach. Many people, including pregnant women, suffer from heartburn or acid indigestion caused by GERD.
Advertisement