Gas exchange - driving force
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 10/29/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC respiratory system cellular metabolism ATP Ventilation Gas Exchange external respiration internal respiration Gas Transport pulmonary circulation systemic circulation driving force
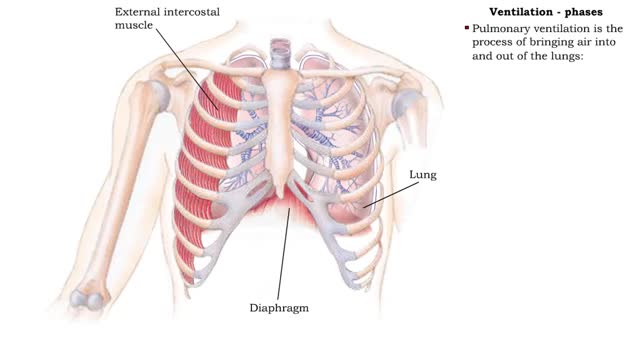
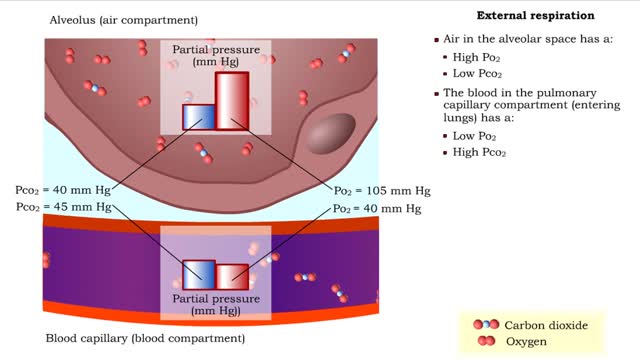
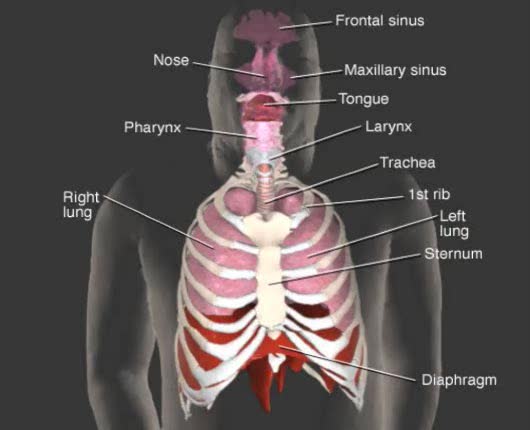
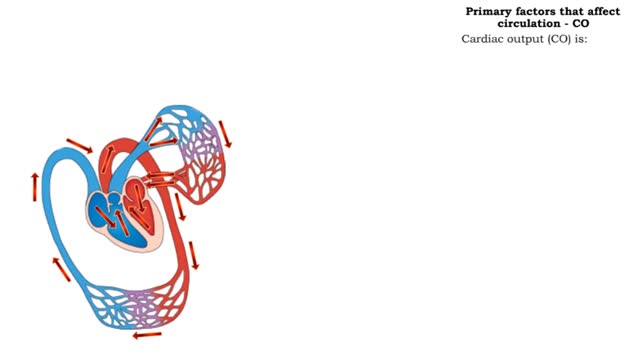
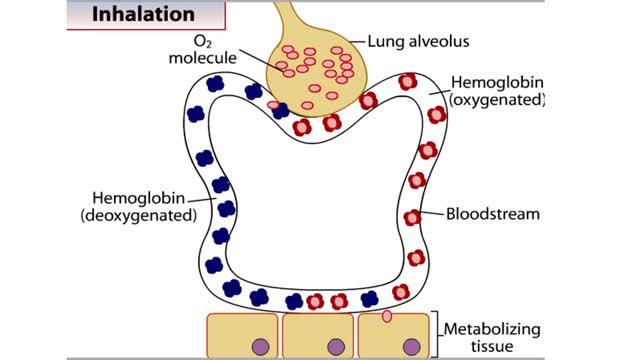
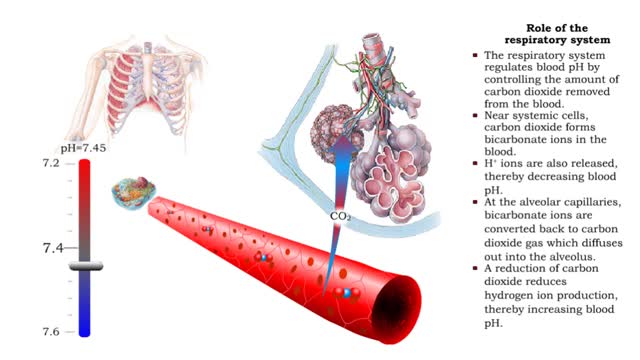
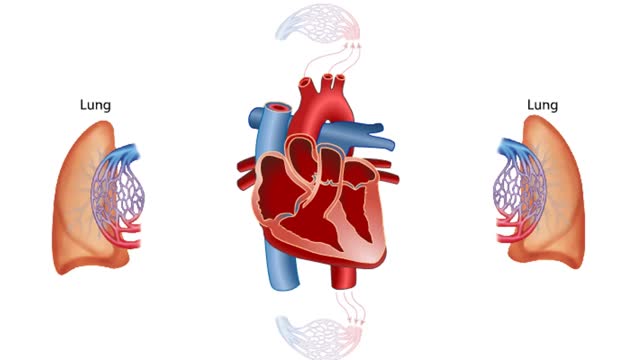
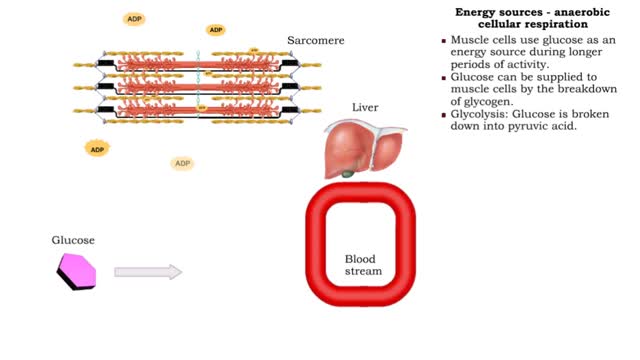
• The respiratory system is responsible for the movement of gases involved in cellular metabolism. • Oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is generated during the aerobic breakdown of glucose and other fuel molecules in order to produce ATP. • Three important continuous physiological processes are responsible for the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide. 1. Ventilation • Moves gases in and out of the lungs. 2. Gas Exchange • The movement of gases into and out of the blood. • Occurs at the lungs (external respiration) and at the tissues (internal respiration). 3. Gas Transport • Blood gases are transported to the lungs (pulmonary circulation). • Blood gases are transported to the organs and tissues throughout the body (systemic circulation). • The direction that a gas moves is dependent on the concentration of that gas. • A gas within a compartment exerts a pressure, which is proportional to the concentration of that gas. • More gas molecules exert a greater pressure. • Gas molecules move down their pressure gradient much like solutes move down their concentration gradient.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.