Control of ventilation rate by other brain centers (posts, hypothalamus & cerebral cortex)
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/03/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Forced ventilation inspiratory area expiratory area internal intercostals Control of ventilation rate by other brain centers ventilation rate. medullary rhythmicity area Apneustic area hypothalamus cerebral cortex
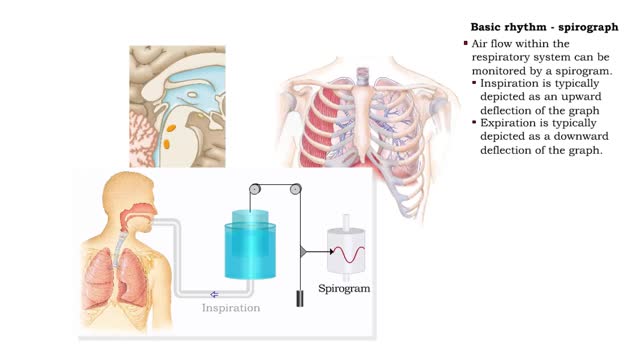
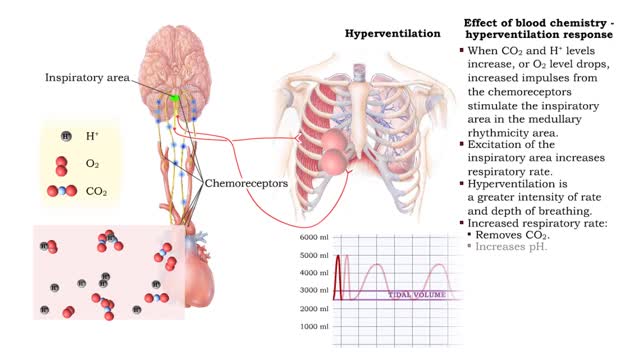
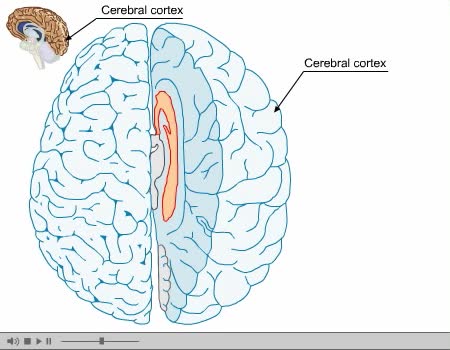
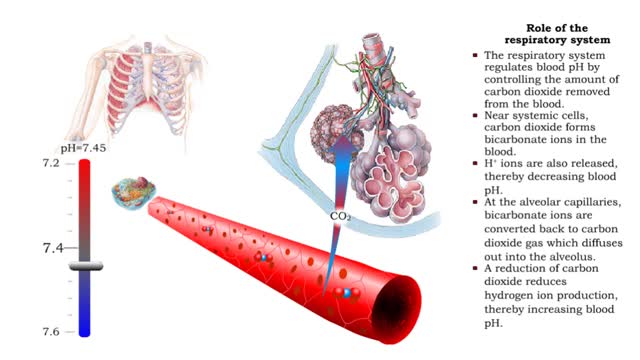
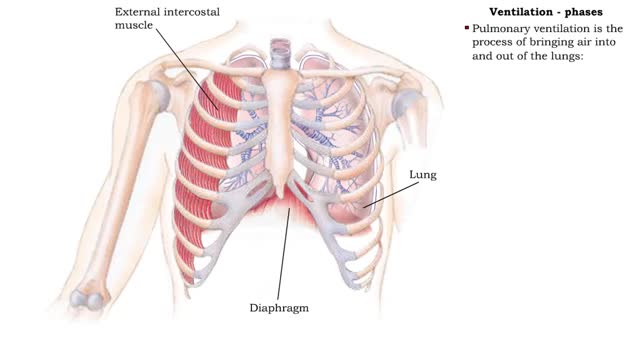
Forced ventilation: • The inspiratory area stimulates accessory inspiratory muscles. • Inspiration is more forceful. • Inspiratory area activates expiratory area, which sends impulses to the expiratory muscles (internal intercostals and abdominal muscles). • Expiration muscles contract, resulting in forced expiration. • Two areas in the pons can modify ventilation rate. • Pneumottudc area: • Inhibits medullary rhythmicity area. • Shortens inspiration phase. • Results in short rapid breathing. • Apneustic area: • Stimulates inspiratory area. • Prolongs the inspiration phase. • Results in slower, deeper breathing. • Hypothalamus: • Emotions, pain and body temperature changes activate centers in the hypothalamus. • These centers, in turn, stimulate the respiratory centers in the pons and medulla, altering the ventilation rate. • Cortical Centers: • Impulses from the cerebral cortex can bypass the respiratory centers in the pons and medulla. • This pathway allows us to consciously alter our breathing patterns.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.