Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/06/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC osmolarity solute concentration nephron urine medullary osmotic gradient antidiuretic hormone ADH Urea cycling vasa recta Henle
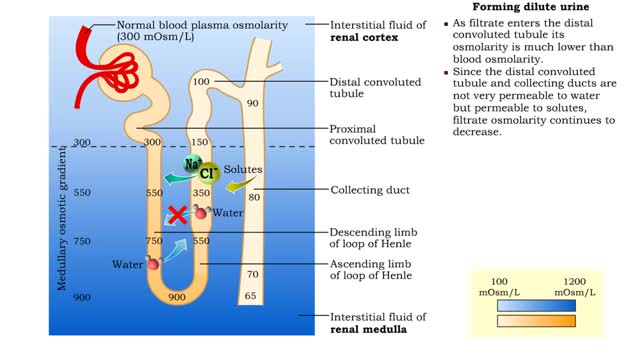
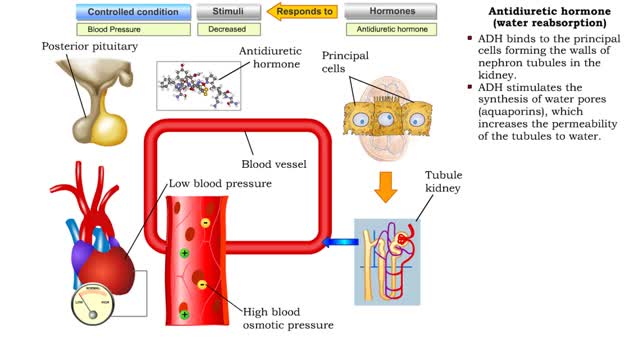
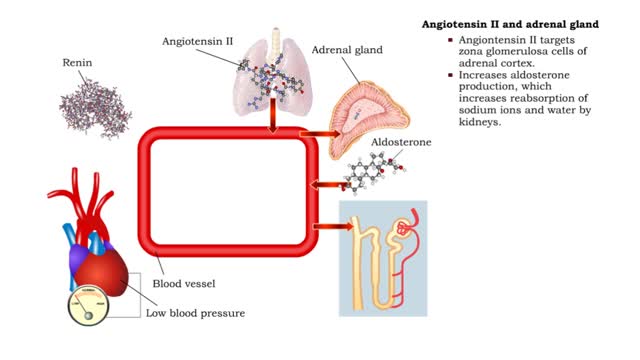
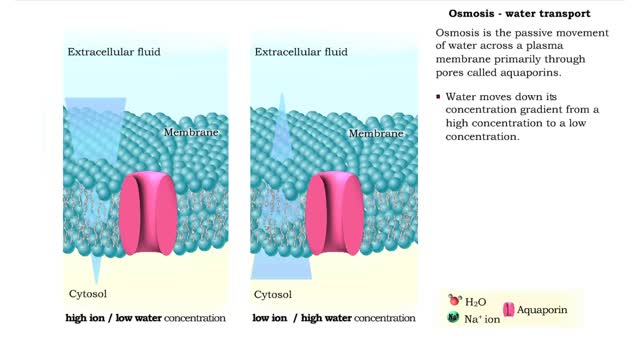
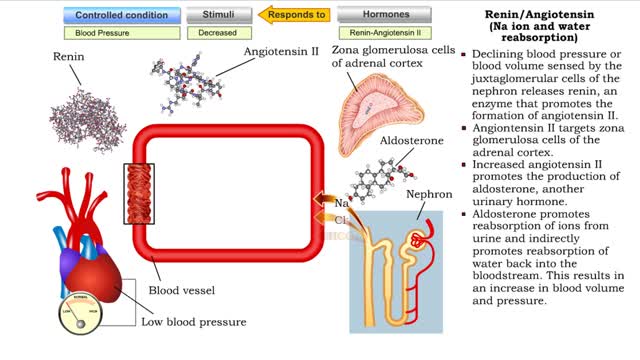
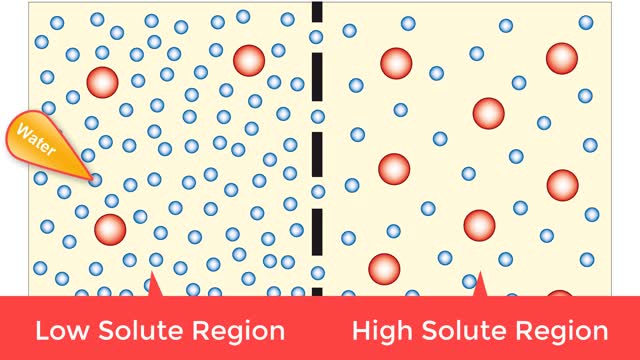
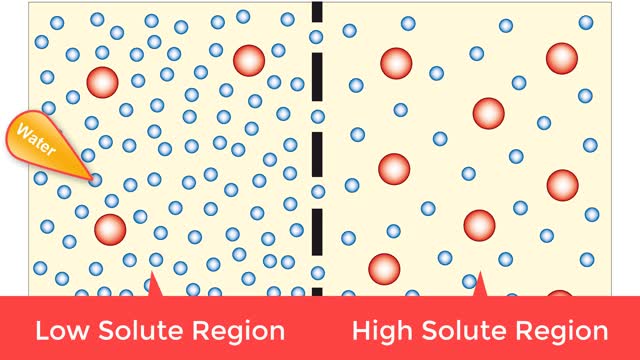
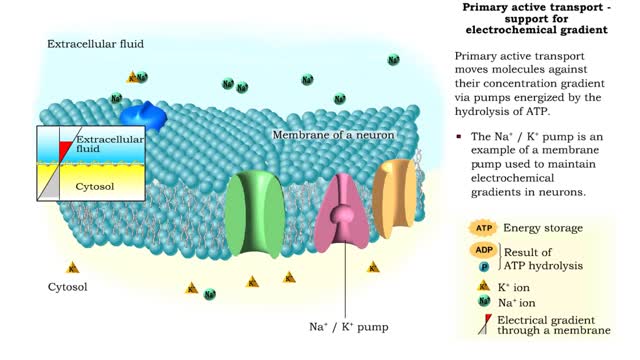
▪ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. ▪ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. • Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter urine composition and volume. ▪ Regulation of osmolarity of body fluids depends on the: • Formation of a medullary osmotic gradient. • Amount of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) present at the collecting ducts. • Both factors allow collecting ducts to reabsorb water and form concentrated urine. • If water is allowed to pass, collecting ducts form dilute urine. • Production of the medullary osmotic gradient depends on three factors: • Differences in water and solute permeability and reabsorption in different sections of the limbs of the loop of Henle. • Urea cycling in the medulla. • Countercurrent exchange in vasa recta.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement




Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.