Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 05/06/2020
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Carbohydrates monosaccharides polysaccharides Glucose condensation reaction glycosidic linkage Amylose Glycogen
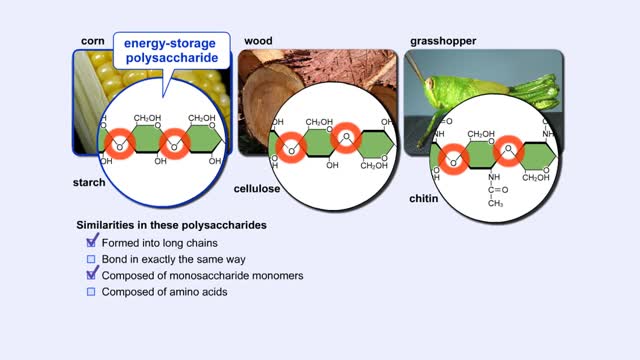
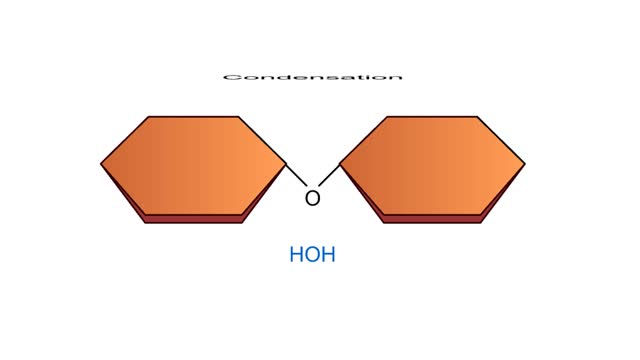
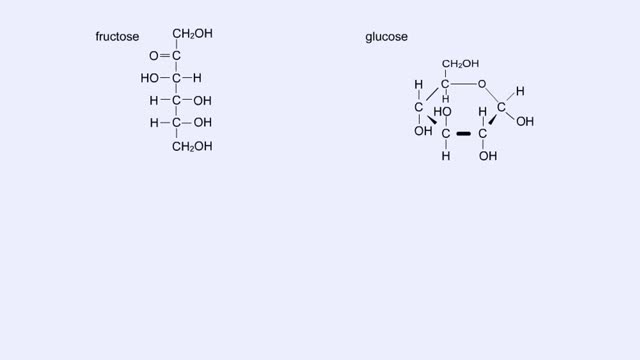
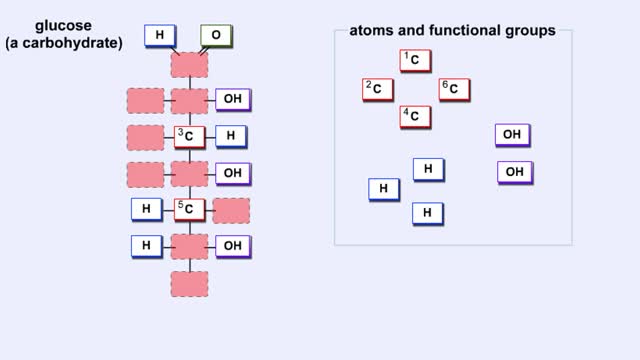
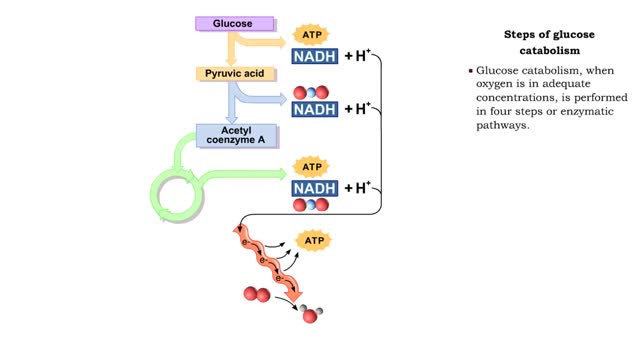
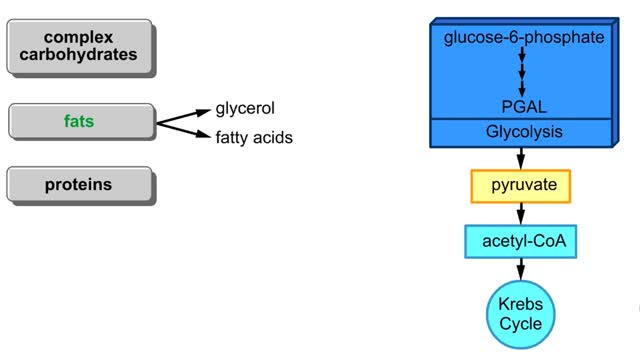
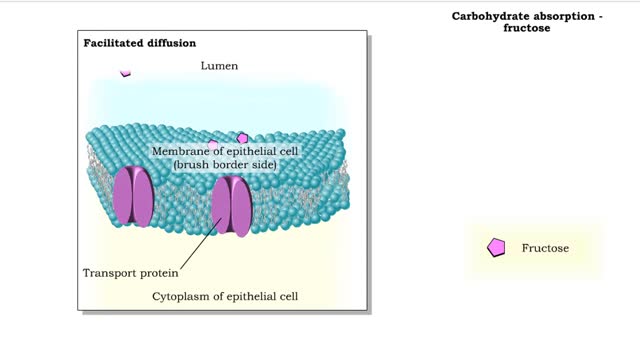
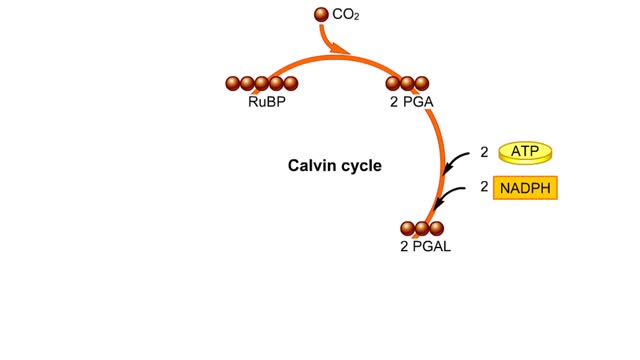
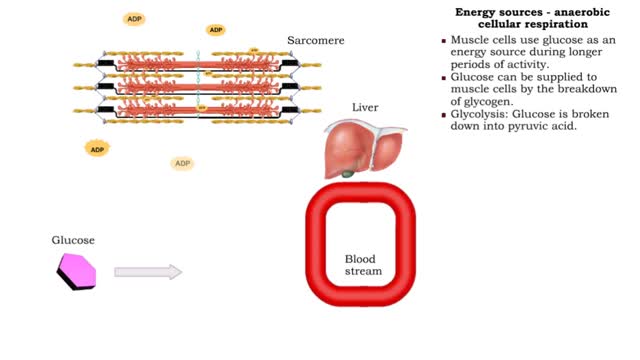
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be added to starch by a condensation reaction. In condensation reactions, two molecules covalently bond to each other and release a water molecule. Here, the bond forms between the 151 carbon of one glucose and the 4th of the other, creating an a-1,4 glycosidic linkage. Branching of new chains can also occur between carbons 1 and 6. Different types of starches are, in fact, distinguished by the amount of branching. Amylose, or plant starch, is not highly branched. Glycogen, by comparison, is highly branched. This polysaccharide is stored in animal livers and muscles. Polysaccharides are forms of stored energy that can be easily hydrolyzed to yield glucose. Glucose can then be further broken down to release energy that is used in cellular activity.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.