Search Results
Results for: 'phosphate functional group'
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10726
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
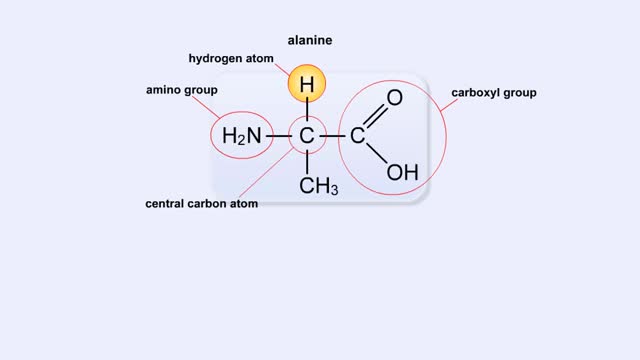
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 10681
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
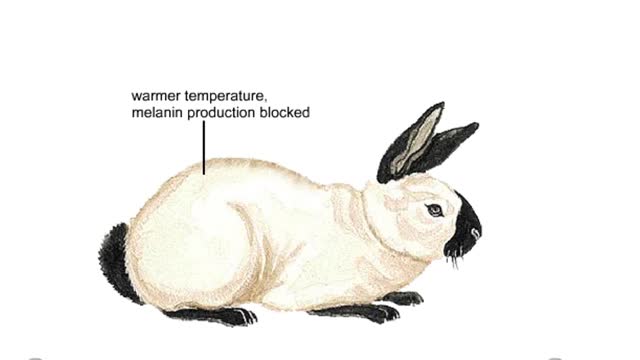
Effect of the environment on coat color in the Himalayan rabbit Animation
By: HWC, Views: 6651
An organism's phenotype—the combination of traits that we observe—is the product of interactions between its genotype and the environment. For example. a Himalayan rabbit is completely white at birth. But within weeks, the fur on the rabbits ears, nose, tail. and lower legs darkens. The...
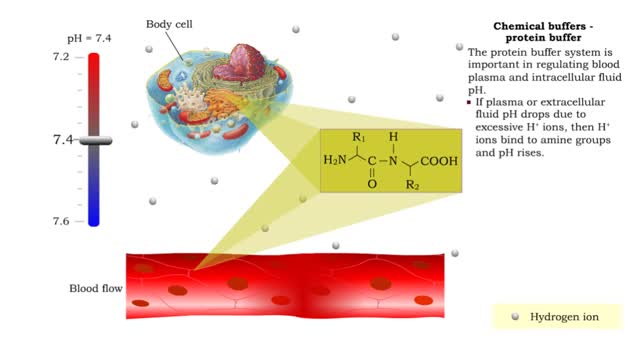
Chemical Buffers - protein buffer, phosphate buffer system and bicarbonate buffer system
By: HWC, Views: 11247
• There are a variety of chemicals in body fluids that prevent the fluids from undergoing large changes in. • These chemicals buffer or regulate fluctuations in H+ concentration. • Chemical buffers: • Bind to H+ ions when there are too many in a solution so pH remains normal. •...
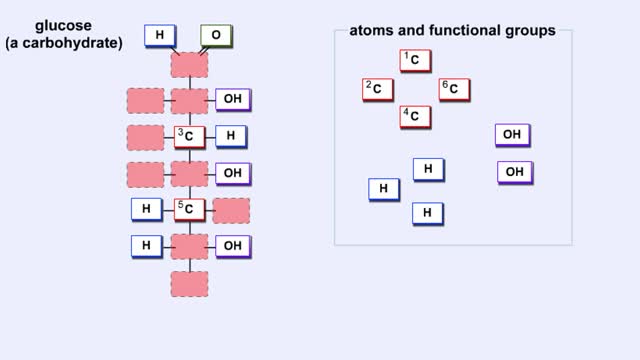
What Are Carbohydrates? Importance of Carbs & High Carb Food
By: HWC, Views: 11227
We hear a lot about carbohydrates in the news. Everybody seems to be on a low-carb diet. The news media often has stories on this diet fad, and companies are busy producing products with reduced carbohydrates. What's this fascination with carbohydrates? In a word: "Diet." The fact is that carb...
Energy inputs and release in glycolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4959
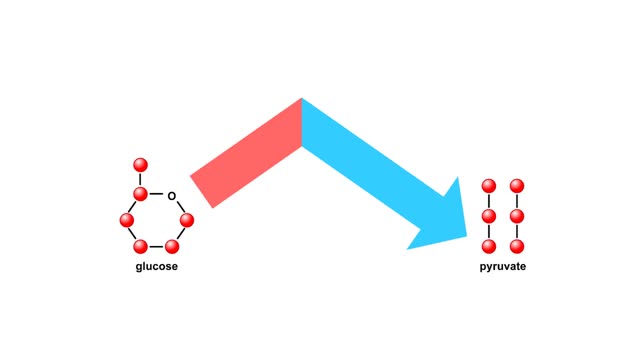
Glycolysis breaks the six-carbon sugar glucose into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. The first steps of glycolysis require an energy input in the form of two phosphate-group transfers from ATP. These phosphorylations raise the energy level of glucose enough to allow the energy-releas...
Peptide Bond Formation Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4859
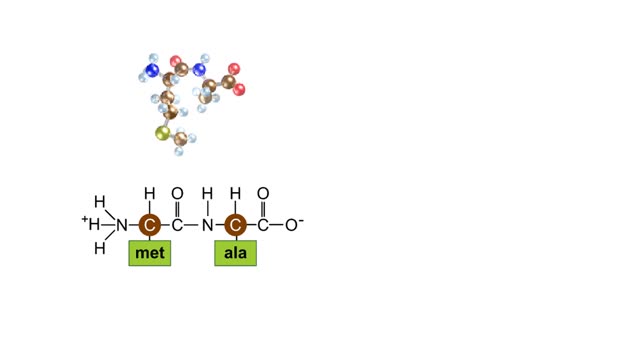
During protein synthesis, peptide bonds link amino acids together in the order specified by DNA instructions. In this case, the first two amino acids in the protein are methionine and alanine. Here are ball-and-stick models of these amino acids. Peptide bond formation is a type of condensatio...
By: HWC, Views: 5294
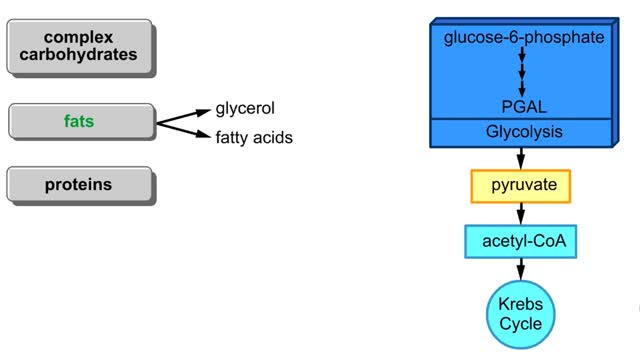
Points at which organic compounds enter the reaction stages of aerobic respiration. Complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose. They become the substrates for glycolysis. If your body doesn't need to burn glucose for energy, glucose-6-phosphate can be co...
By: HWC, Views: 11276
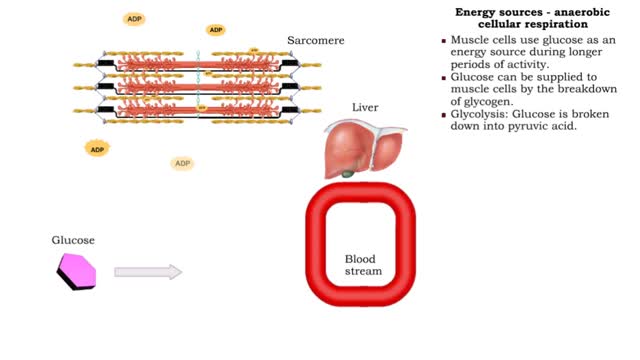
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen syste...
Advertisement