Regulation of GFR: three methods, autoregulation & autoregulation via myogenic mechanism
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 11/04/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Regulation of GFR glomerular capillaries Renal autoregulation Nervous regulation Hormonal regulation sympathetic neuron afferent arteriole mesangial cells renal tubule ascending limb of loop of Henle macula densa efferent arteriole autoregulation autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism afferent arterioles stretch GFR decreases
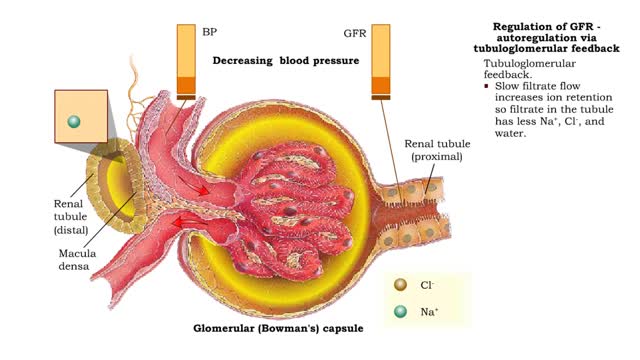
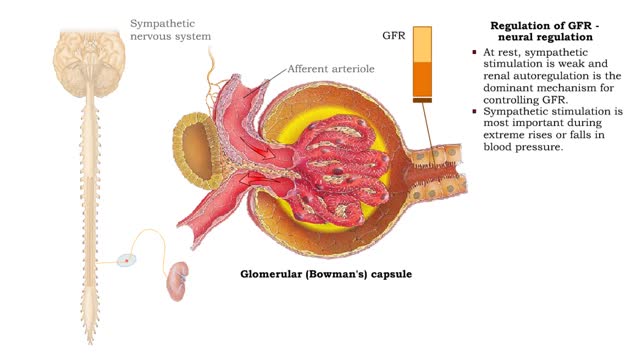
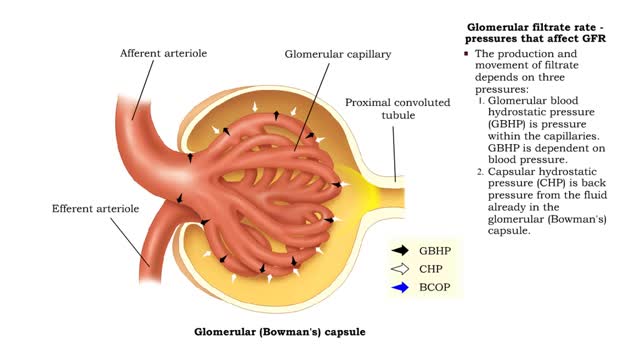
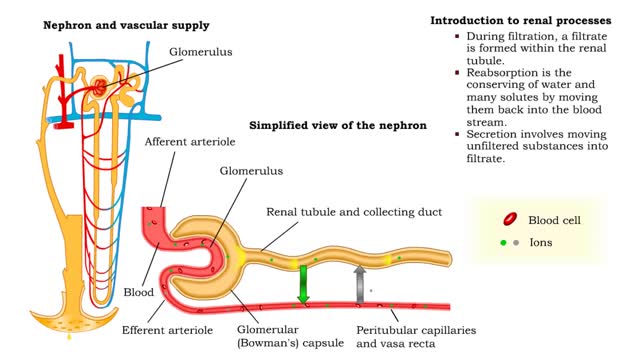
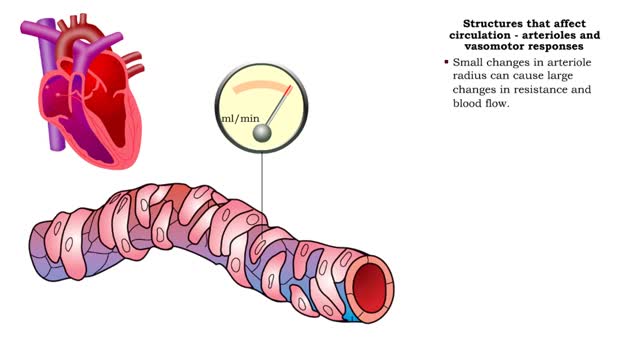
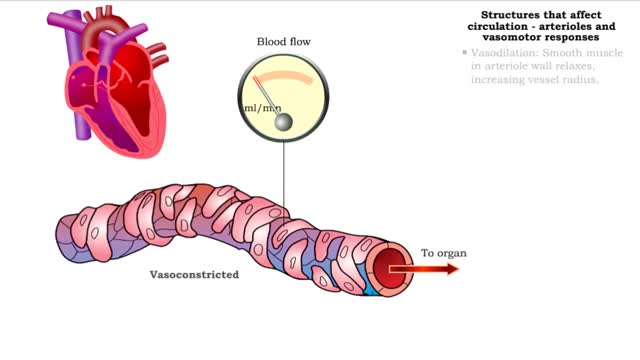
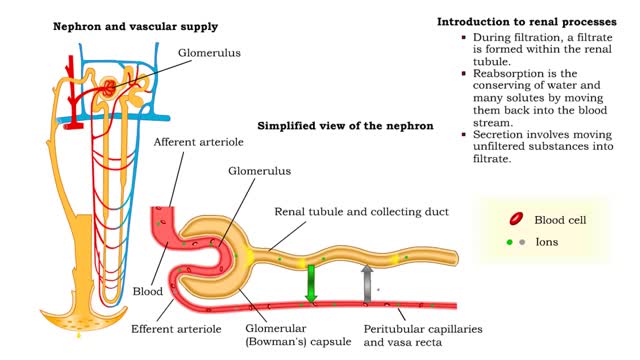
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Hormonal regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when the kidneys themselves regulate blood flow. • Two renal autoregulatory mechanisms maintain normal GFR over a wide range of systemic blood pressures. • As systemic blood pressure goes up, the smooth muscle cells in the afferent arterioles stretch. • The smooth muscle fibers of the afferent arterioles respond to stretching by contracting, reducing blood flow to the glomerular capillaries. • GFR decreases. • As systemic blood pressure goes down, the smooth muscle cells in the afferent arteriole relax. • The relaxation of the afferent arteriole allows greater blood flow to the capillaries. • GFR increases.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement




Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.