Search Results
Results for: 'glucose catabolism'
By: HWC, Views: 11965
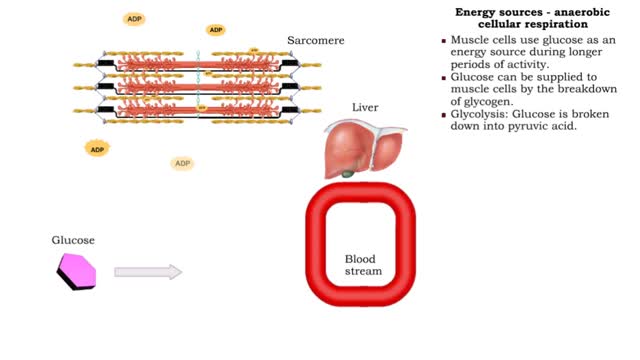
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen syste...
By: HWC, Views: 11491
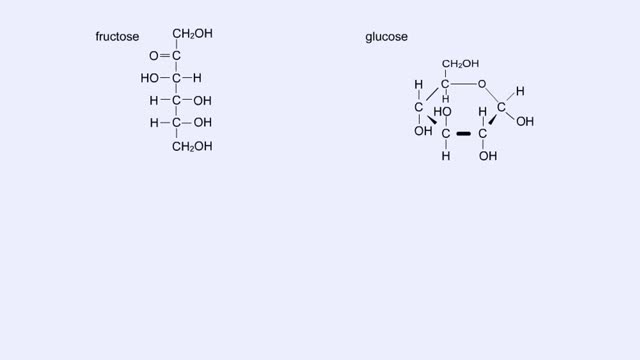
Here are the molecular structures of three simple sugars: glucose, ribose, and fructose. Look at these simple sugars and identify what characteristics they all share. As you can see, all of the carbohydrates have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 and there is always a double bo...
By: HWC, Views: 12012
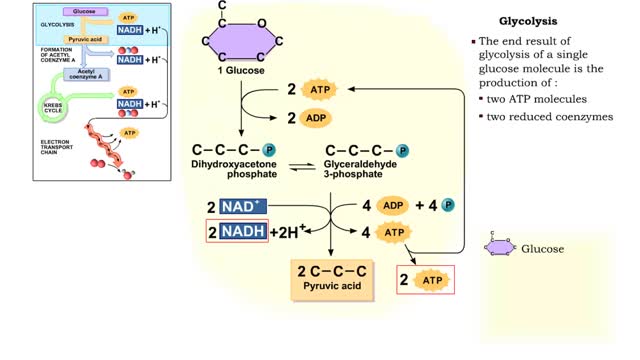
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Hormonal regulation of pregnancy - weeks 17 through 38
By: HWC, Views: 11988
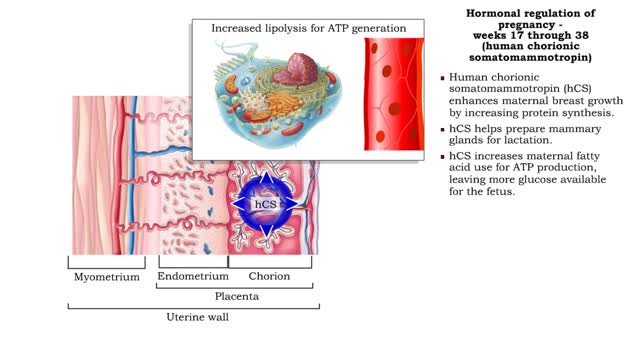
• Estrogens increase uterine blood flow, maintaining the endometrium during pregnancy. • High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit the synthesis of milk. Progesterone inhibits myometrial contractions of the uterus to prevent premature birth. • Relaxin inhibits myometrial contract...
By: HWC, Views: 11551
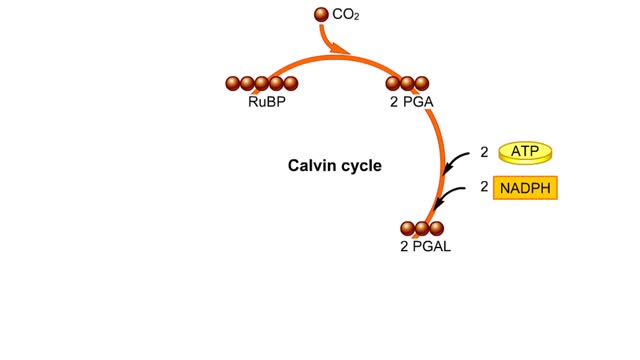
he light-independent reactions make sugars by way of a cyclic pathway called the Calvin cycle. The cycle begins when rubisco attaches a carbon from carbon dioxide to ribulose bisphosphate. The molecule that forms splits into two molecules of PGA. Each PGA gets a phosphate group from ATP a...
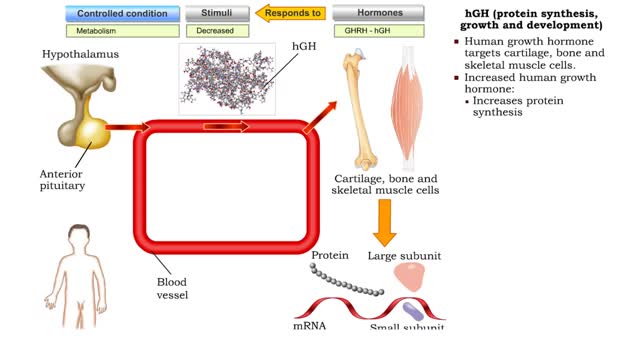
hGH (protein synthesis, growth and development)
By: HWC, Views: 12108
• Increased GHRH, a hypothalamic releasing hormone stimulated by low blood glucose, physical exertion, and increased sympathetic stimulation, stimulates the production of human growth hormone (hGH) from the somatotrophic cells of the anterior pituitary. • Human growth hormone targets cartil...
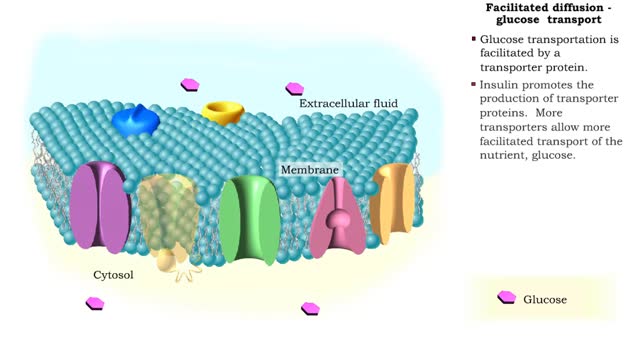
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11959
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
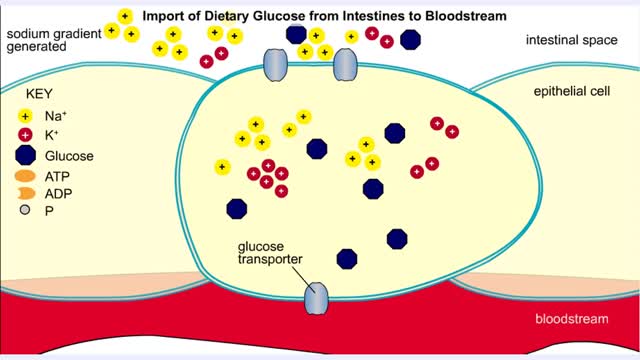
Import of Dietary Glucose from Intestines to Bloodstream
By: HWC, Views: 11147
• Membranes have hydrophobic interiors. which resist the passage of hydrophilic compounds and ions. • However. transporter membrane proteins facilitate the passage of these molecules. • Passive transporters accelerate diffusion of molecules towards equilibrium (decrease a concentrat...
By: Administrator, Views: 16448
Hyperglycemia means high (hyper) glucose (gly) in the blood (emia). Your body needs glucose to properly function. Your cells rely on glucose for energy. Hyperglycemia is a defining characteristic of diabetes—when the blood glucose level is too high because the body isn't properly using or doesn...
Advertisement